
Our group is conducting theoretical research on various properties of quantum materials. The aim of our research is to understand their microscopic mechanism on the basis of quantum mechanics and statistical physics. In particular, we are interested in phase transitions and related quantum phenomena where electron correlations play an essential role. Through material-oriented research, we are striving to develop a systematic and comprehensive understanding of diverse phenomena and promote materials design and predictions of new quantum properties.
We welcome motivated students and postdocs. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us and visit our lab!
Research
Materials science in strongly correlated systems - toward understanding and exploration of novel quantum phenomena
main targets
- materials: strongly-correlated electron systems (transition metal compounds, rare-earth compounds, organic conductors, ...), surfaces/Interfaces, nano structures, ...
- phenomena: electron correlation, metal-insulator transition, magnetism, critical phenomena, charge-spin-orbital degrees of freedom, geometrical frustration, spin liquid, topology, self-organization, dynamics, ...
main topics
- a variety of phenomena through interplay among charge, spin, and orbital degrees of freedom
- novel quantum phenomena caused by cooperation of electron correlation and spin-orbit coupling
- peculiar properties brought by frustration and topology
- high-order correlations under strong fluctuations, and their new excitations and dynamics
- new phenomena in surfaces/interfaces, disorder, and nano-scale structures
- development and improvement of computational algorithms, etc.
Strongly correlated systems
Systems composed of many particles that interact strongly with each other are called "strongly correlated system". In a class of substances, strongly correlated systems are realized by electrons that feel the strong Coulomb repulsive force of each other. There, unlike ordinary metals and semiconductors, electrons cannot move around freely, and sometimes they cannot move at all. In such a situation, various "faces" that are not found in free electrons appear in the material properties in an unexpected way.
In our group
We are conducting theoretical research on such unconventional properties of the strongly correlated electron systems. Such a research is a super-difficult problem categorized into "quantum many-body problems", in which electrons of an Avogadro number of electrons moving according to quantum mechanics must be dealt with. It is an impossible task to completely follow the motion of all the electrons by our present technologies. Therefore, we are confronting this super-difficult problem by making full use of quantum mechanics, statistical mechanics, cutting-edge theory, rapidly evolving computers and numerical algorithms.
Our research targets are wide-ranging, including transition metal compounds in which d-electrons play a leading role, rare-earth compounds in which f-electrons play a leading role, and molecular conductors with organic molecules as units. Beyond the conventional wisdom, we are trying to discover interesting problems and work on them intensively. The main research methods are complementary ones by combining first-principles calculations reflecting actual material situations, construction of theoretical models capturing the essence of the phenomena, and numerical simulations and analytical calculations. When the existing methods are not sufficient to solve the problems, we will also work on the development of new calculation methods and numerical algorithms.
Toward new horizon in materials science
In addition to pursuing interest in fundamental physics, we also aim to establish a theoretical framework that has the potential to be useful in future applications, such as electronics and quantum information based on strongly correlated physics. The goal of our research is to elucidate the universality of the quantum many-body problem in strongly correlated electron systems by conducting research that is closely related to real substances and systematically understanding the individuality of each material. Furthermore, through such understanding, we aim to open up new horizons in materials science, such as the design of new materials and the prediction of new physical properties.
Highlight
Click the thumbnail to show/hide the description below.




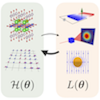
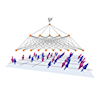
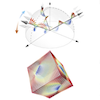




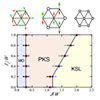
Exploration of Majorana particles via spin current in Kitaev quantum spin liquids

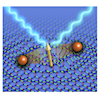
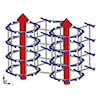
In quantum spin liquids, which are exotic quantum states in magnetic materials, spin excitations split into several different quasiparticle excitations. In Kitaev-type quantum spin liquids, spin excitations split into Majorana particles, but capturing evidence of this is experimentally challenging, making the development of new detection methods an urgent task. This study focuses on spin currents used in the field of spintronics and investigates the possibility of generating spin currents through thermal gradients in Kitaev quantum spin liquids. As a result, we discover that in the quantum spin liquid state of the Kitaev model, spin currents are generated despite Majorana particles having no angular momentum, and the direction of these currents changes depending on the sign of the Kitaev-type interactions. Furthermore, we propose an experimental detection method by comparing with spin currents carried by magnons in conventional ferromagnetic states. The results of this study not only propose a new method for identifying Kitaev quantum spin liquids but also contribute to the development of new spintronics using quantum spin liquids.
Y. Kato, J. Nasu, M. Sato, T. Okubo, T. Misawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. X 15, 011050 (2025)
Press Release
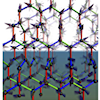
Driving magnetic torons by an electric current

Magnetic skyrmions, a type of topological magnetic structure, generate various quantum transport phenomena due to the emergent electromagnetic fields arising from their unique spin structures. Magnetic skyrmions have a three-dimensional string-like structure, and when they break, they form a magnetic structure called a magnetic toron, which has magnetic hedgehogs at both ends. In this study, we investigate the dynamics of a topological magnetic crystal made of the magnetic torons when an electric current is applied. As a result, we find that, similar to magnetic skyrmions, magnetic torons are driven along the current and exhibit Hall motion, being driven in a direction perpendicular to the current. Furthermore, we discover that the Hall motion of magnetic torons can be widely controlled by changing the strength of the current and magnetic field; the Hall angle, representing the deviation from the current direction, ranges from zero to ninety degrees. We clarify that this unique property, not observed in skyrmions, is due to the characteristic magnetic structure of the magnetic torons and the potential of the underlying lattice structure. The results of this study provide new directions for spintronics using topological magnetic structures.
K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Commun. Phys. 8, 69 (2025)
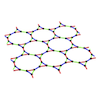
Realization of Kitaev spin liquid in van der Waals heterostructures

To realize the quantum spin liquid that appears in the theoretical model called the Kitaev model, various candidate materials are being explored. Among them, α-RuCl3 has been intensively studied as a promising candidate material, but the need to apply a magnetic field to realize the quantum spin liquid state has hampered both experimental and theoretical studies. In this study, focusing on the fact that α-RuCl3 is a van der Waals material, we investigate the possibility of the quantum spin liquid in heterostructures with other van der Waals magnetic materials. As a result, we find that in the heterostructure with the ferromagnetic material CrBr3, the internal magnetic field from the CrBr3 layer stabilizes the quantum spin liquid state in the α-RuCl3 layer at zero magnetic field. Furthermore, in the heterostructure with another ferromagnetic material CrI3, we clarify that the system tends towards metallization. The results of this study indicate that the realization of Kitaev-type quantum spin liquids and their metallization are possible by utilizing the proximity effects in van der Waals heterostructures, providing new guidelines for material design of the Kitaev model.
L. Zhang and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 110, L241109 (2024)
Spin liquid crystal meets spin liquid

Liquid crystals are states that possess properties intermediate between those of solids and liquids. In magnetic materials, spin arrangements can take on liquid crystal-like states, and their unique magnetic properties have attracted attention. In particular, it is an important task to elucidate the transitions between spin liquids, where spin arrangements behave like liquids, and magnetic ordered states, where they behave like solids. In this study, we investigate the competition and cooperation between these states in a spin model where all three states—solid, liquid, and liquid crystal—can appear. As a result, we discover several new magnetic states, including those where spin arrangements become non-coplanar, in regions where both states compete. Notably, we find that a chiral spin liquid, which is a liquid-like state that breaks time-reversal symmetry, appears at finite temperatures. The results of this study are significant in clarifying the relationship between spin solids, liquids, and liquid crystals, and in pioneering new magnetic phenomena arising from their competition and cooperation.
R. Pohle, N. Shannon, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Research 6, 033077 (2024)
R. Pohle, N. Shannon, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 107, L140403 (2023)
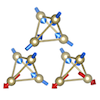
Inverse design of Hamiltonian with desired properties using automatic differentiation
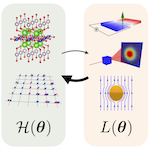
In the field of machine learning, neural networks optimize a numerous variables employing an algorithm known as automatic differentiation via the backpropagation. This automatic differentiation is applicable not only in neural networks, but also across a broad range of numerical methods. In the present study, we employ automatic differentiation to optimize numerous variables embedded within a Hamiltonian so as to achieve the targeted physical properties. This leads to the automatic disign of new models, which has demonstrated compelling results. For instance, we have successfully generated Hamiltonians that display large quantum anomalous Hall effects or produce considerable photocurrent under solar radiation. Our framework is expected to contribute to the discovery of unprecedented materials and principles, going beyond conventional material and model design based on experience and intuition, as it is highly versatile and enables automatic search in vast variable spaces.
K. Inui and Y. Motome, Commun. Phys. 6, 37 (2023)
K. Inui and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Research 6, 033080 (2024)
Press Release
YouTube
Machine learning quantum many-body states by neural network
Neural network, which can in principle approximate any function, has recently garnered attention as a new tool to study quantum many-body systems. In fermionic systems, most of the previous studies rely on the Slater determinant to implement the sign change associated with particle exchange, but it hampers large-scale calculations since the numerical cost is O(N3) for the number of particles N. In the present study, we develop a general framework to approximate fermionic many-body wave functions by neural networks without using the Slater determinant. In our method, the sign changes of the wave function are explicitly calculated for each particle exchange in real space, while the rest part is approximated by the fully-connected neural networks. This reduces the numerical cost from O(N3) to O(N2) or less. We apply this framework to the Hubbard model on a two-dimensional square lattice, and demonstrate that the numerical accuracy can be better than the previous results. Our finding would contribute to the rapidly growing field of neural network quantum states.
K. Inui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Research 3, 043126 (2021)
Topological transition and emergent electromagnetic phenomena in spin moire
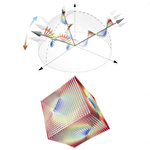
Topological spin textures such as magnetic skirmions and hedgehogs have attracted much attention due to the topological robustness and nontrivial quantum transport phenomena through the emergent electric and magnetic fields. To control the topological properties in these spin textures is an important issue in not only fundamental physics but also device applications. In the present study, regarding the topological spin textures as moire patterns by spin helices, we study the effects of modulations of the amplitudes, relative angles, and phases of the superposed waves. We find that the modulations lead to motions of the topological defects, i.e., magnetic hedgehogs and antihedgehogs, and their pair annihilation accompanied by singular behavior in the emergent electric and magnetic fields. Furthermore, an external magnetic field and an anisotropy in the system can induce such topological changes. Our results provide a new perspective from the spin moire picture on the rapidly growing field and contribute to the exploration of new control of topological nature and emergent electromagnetic phenomena in the topological spin textures.
K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 103, 054427 (2021)
K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 103, 184421 (2021)
K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 105, 224405 (2022)
Magnetic hedgehog lattice in chiral metals
Chiral magnets with broken spatial inversion symmetry often exhibit peculiar magnetic properties with a spiral twist in the direction of magnetic moments, which profoundly affect the motion of electrons. Recently, hedgehog-like magnetic structures were discovered experimentally, but the stabilization mechanism has not been clarified yet. In the present study, by performing theoretical calculations focusing on the higher-order exchange interactions generated by electron motion, we elucidate the microscopic mechanism for hedgehog lattices composed of periodic arrays of the hedgehogs. Furthermore, we show that in an applied magnetic field the system undergoes various phase transition phenomena including topological transitions caused by pair annihilation of the hedgehogs. Since the magnetic hedgehogs can be regarded as magnetic monopoles that produce an effective magnetic field for electrons, they have the potential to give a significant impact on electron transport phenomena. Our results would contribute to further development of such emergent electromagnetic phenomena and new quantum transport.
S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 101, 144416 (2020)
S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, JPS Conf. Proc. 30, 011010 (2020)
See also
S. Hayami and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 33, 443001 (2021) [TOPICAL REVIEW]
Spin current generation that does not require the spin-orbit coupling
Most of the electronic devices that support modern society operate using an electric current, which is the flow of electric charge of electrons. If it can be replaced with a spin current, which is the flow of electron spins, one may realize ultimate energy-saving devices without energy loss due to heat generation. Most of the mechanisms that generate spin currents thus far have been based on the spin-orbit coupling that intertwines the electron orbital motion and spin. In the present study, focusing on the molecular orientation pattern in organic compounds, we discover a completely new mechanism for spin current generation that does not require the spin-orbit coupling. We show that the conversion efficiency to spin current by this mechanism is comparable to the value by the conventional mechanism for a typical compound Pt. Since this new mechanism arises from the lattice symmetry and a simple antiferromagnetic order, it is expected to be realized in various materials. Our result would expand the research area for spintronics materials and promote further application to electronic devices.
M. Naka, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, Y. Yanagi, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, Nat. Commun. 10, 4305 (2019) [Editors’ Highlights]
M. Naka, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, Y. Yanagi, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, Phys. Rev. B 102, 075112 (2020)
M. Naka, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, Phys. Rev. B 103, 125114 (2021)
M. Naka, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, Phys Rev. B 106, 195149 (2022)
See also
M. Naka, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, npj Spintronics 3, 1 (2025) [Review]
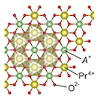
Materials design of Kitaev magnets in f-electron compounds
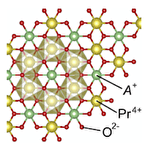
The Kitaev model, which has bond-dependent anisotropic interactions, provides a new guiding principle for realizing a quantum spin liquid. Thus far, several candidate materials have been found in 5d and 4d electron systems, such as Ir and Ru compounds, but they are still limited. In the present study, to exploring new platform of the Kitaev spin liquid, we investigate a class of f-electron systems, by using first-principles calculations and model calculations. As a result, we clarify that in honeycomb-layered materials A2PrO3 (A is an alkali metal), an antiferromagnetic Kitaev-type anisotropic exchange interaction is realized between the Pr4+ ions in the 4f1 electronic state. This is in stark contrast to the ferromagnetic ones in the d-electron candidates. We elucidate that the small crystal-field splitting in the f-electron systems and spatial anisotropy peculiar to the f orbitals play an important role in the antiferromagnetic Kitaev-type interaction. Our results would contribute to not only the expansion of the range of candidate materials but also the exploration of the Kitaev spin liquid in unexplored parameter regions.
S.-H. Jang, R. Sano, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 99, 241106(R) (2019)
S.-H. Jang, R. Sano, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Materials 4, 104420 (2020)
S.-H. Jang and Y. Motome, Commun. Mater. 5, 192 (2024)
S.-H. Jang and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 110, 155124 (2024)
See also
Y. Motome, R. Sano, S.-H. Jang, Y. Sugita, and Y. Kato, J. Phys: Condens. Matter 32, 404001 (2020) [Special Issue on Quantum Spin Liquids]
求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 52, 199 (2017); 53, 305 (2018); 54, 217 (2019); 57, 297 (2020)
張 成燻、求 幸年:固体物理 57, 757 (2022)
Multiple Dirac cones in atomically-thin honeycomb materials
The discovery of monolayer graphen has initiated two important fields, science of atomically-thin materials and Dirac semimetals. They have been rapidly growing, and recently, topological states of matter have been intensively studied for atomically-thin transition metal compounds. In these systems, novel topological states may be stabilized by the interplay between charge, spin, and orbital degrees of freedom under strong electron correlations. In the present study, we theoretically explore such novel properties in eg electron states of the transition metals, by using ab initio calculations and model analyses. We find that monolayer transition-metal trichalcogenides with a honeycomb structure exhibit eight independent Dirac cones, and the system can turn into a topological ferromagnetic state with a high Chern number under the spin-orbit coupling and electron correlations. Furthermore, we elucidate that various types of topological phases and transitions between them are realized in a wide range of atomically-thin honeycomb materials with eg electrons.
Y. Sugita, T. Miyake, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 97, 035125 (2018) [selected in Kaleidoscope]
Y. Sugita, T. Miyake, and Y. Motome, Physica B: Condensed Matter 536, 48 (2018)
Y. Sugita and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 99, 041101(R) (2019)
Soliton lattice in chiral magnets
In monoaxial chiral magnets, which has left- and right-handed degrees of freedom along a specific axis in the crystals, a helimagnetic state is partially relaxed by applying a magnetic field perpendicular to the chiral axis, and it can turn into the so-called chiral soliton lattice with a periodic array of soliton-like spin helices. Since the pioneering works by Dzyaloshinskii in 1960's, extensive studies have been done for a long time, and recently, the chiral soliton lattice was observed by using real-space probes, which has accelerated the researches from both theories and experiments. Theoretically, however, there are less studies including the lattice discreteness and itinerant electron degrees of freedom. Here, we consider a model including the itinerant electrons for such monoaxial chiral magnets, and study the ground-state and finite-temperature properties by using variational calculations and Monte Carlo simulations, respectively. We successfully explain the experimental results of the nonlinear negative magnetoresistance and the lock-in of the period of chiral soliton lattices in an applied magnetic field. These results would contribute to further development of the cooperative studies between theories and experiments on this rapidly growing topic.
S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 86, 063701 (2017)
S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 87, 033708 (2018)
S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Physica B: Condensed Matter 536, 223 (2018)
Kitaev-Heisenberg model in d7 high-spin systems
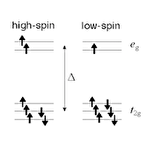
The Kitaev model proposed by A. Kitaev in 2006 is a localized spin model that realizes an exact spin liquid ground state. Since Jackeli and Khaliullin pointed out that the model could give a good description of some spin-orbit coupled Mott insulators in the d5 low-spin state, 5d- and 4d-electron systems, such as Ir and Ru compounds, have been intensively studied as the Kitaev candidates. However, the researches of the Kitaev spin liquids have been mostly limited to such d5 low-spin systems thus far, and the candidate materials are still limited. In order to explore a new platform of the Kitaev spin liquids, we here investigate the possibility of realizing the Kitaev model in the d7 high-spin state. We find that, similar to the d5 low-spin case, the d7 high-spin systems can realize spin-orbit coupled Mott insulators with the effective magnetic moment 1/2, and the low-energy effective model is given by the Kitaev-Heisenberg model with the anisotropic Kitaev-type interactions and the isotropic Heisenberg exchange interactions. Our results would contribute to provide a new playground for the Kitaev spin liquids beyond the d5 low-spin systems.
R. Sano, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 97, 014408 (2018)
See also
Y. Motome, R. Sano, S.-H. Jang, Y. Sugita, and Y. Kato, J. Phys: Condens. Matter 32, 404001 (2020) [Special Issue on Quantum Spin Liquids]
求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 52, 199 (2017); 53, 305 (2018); 54, 217 (2019); 57, 297 (2020)
張 成燻、求 幸年:固体物理 57, 757 (2022)
Three-dimensional chiral spin liquid transition
The chiral spin liquid is a category of quantum spin liquids where the time reversal symmetry is spontaneously broken. This exotic magnetic state has been extensively studied, especially in two dimensions, in the context of the high TC superconductivity, the fractional quantum Hall effect, frustrated quantum magnets, etc. However, much less is known for three dimensions (3D). Here, we consider the chiral spin liquids in an extension of the exactly-soluble Kitaev model to 3D. In particular, we study finite-temperature properties of the model on a hypernonagon lattice with nine-site elementary loops. By performing Monte Carlo simulations for the effective models associated with Z2 fluxes defined on each loop, we find a finite-temperature phase transition between the paramagnetic state and the chiral spin liquid. This is the first unbiased results on finite-temperature properties of the 3D chiral spin liquids to our knowledge, which would significantly contribute to the future study of the exotic states.
Y. Kato, Y. Kamiya, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 96, 174409 (2017)
P. A. Mishchenko, Y. Kato, K. O'Brien, T. A. Bojesen, T. Eschmann, M. Hermanns, S. Trebst, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 101, 045118 (2020) [Editors' Suggestion]
See also
Y. Motome and J. Nasu, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 89, 012002 (2020) [INVITED REVIEW PAPER]
求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 52, 199 (2017); 53, 305 (2018); 54, 217 (2019); 57, 297 (2020)
Magnetic skyrmion with a high topological number
Magnetic skyrmions are microscopic swirling textures composed of electron spins in solids. Owing to the topologically protected nature and a variety of responses to electric and magnetic fields, they have attracted much attention for potential applications to new magnetic devices. Thus far, magnetic skyrmions with topological number of unity, which are stable in an applied magnetic field, have been extensively studied, but it has been desired to realize new types of skyrmions for further extending the possibility of applications. We here show that a skyrmion crystal with unusually high topological number of two is stabilized in itinerant magnets at a zero magnetic field. The results are obtained for a minimal Kondo lattice model by an unrestricted large-scale numerical simulation. Furthermore, we find that the topological number can be switched successively by a magnetic field from 2 to 1, and to 0. Our results will stimulate new fundamental scientific principles for potential applications, such as multiple digital switching memory by a weak magnetic field.
R. Ozawa, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 147205 (2017)
S. Hayami, R. Ozawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 95, 224424 (2017) [selected in Kaleidoscope]
Press release
See also
S. Hayami and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 33, 443001 (2021) [TOPICAL REVIEW]
Magnetization curve and magnetoelectric behavior from antiferromagnetic square cupolas
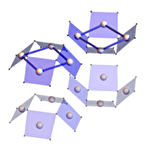
Systems without spatial inversion and time reversal symmetry often exhibit cross correlations between magnetism and electricity (linear magnetoelectric effects). As a new playground of such interesting phenomena, a recently synthesized Cu oxide Ba(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4 has attracted much attention. The lattice structure of this compound is composed of an assembly of low-symmetric units Cu4O12 forming square cupolas, where spatial inversion symmetry is broken locally. In addition, localized magnetic moments at Cu sites exhibit a magnetic long-range order at low temperature, which breaks time reversal symmetry as well. These lead to a magnetoelectric effect of quadrupole type, and indeed, a dielectric anomaly was observed. We here construct a minimal theoretical model, which successfully reproduces the full magnetization curves measured at the Institute for Solid State Physics, University of Tokyo. Our model points to an importance of the antisymmetric exchange interaction called the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction arising from the low symmetry of square cupolas. Furthermore, elaborating the ground-state and finite-temperature phase diagrams of the model, we predict five different antiferromagnetic phases. As different types of magnetoelectric behaviors are expected in each phase, further experiments in the high magnetic field regime are currently in progress.
Y. Kato, K. Kimura, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, A. Matsuo, K. Kindo, M. Akaki, M. Hagiwara, M. Sera, T. Kimura, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 107601 (2017)
K. Kimura, Y. Kato, K. Yamauchi, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, A. Matsuo, K. Kindo, M. Akaki, M. Hagiwara, S. Kimura, M. Toyoda, Y. Motome, and T. Kimura, Phys. Rev. Materials 2, 104415 (2018) [Editors' Suggestion]
Y. Kato, K. Kimura, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, A. Matsuo, K. Kindo, M. Akaki, M. Hagiwara, S. Kimura, T. Kimura, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 99, 024415 (2019)
K. Kimura, Y. Kato, S. Kimura, Y. Motome, and T. Kimura, npj Quantum Mater. 6, 54 (2021)
T. Katsuyoshi, K. Kimura, Z. Yang, Y. Kato, S. Kimura, Y. Motome, Y. Kohama, and T. Kimura, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 90, 123701 (2021) [Papers of Editors' Choice]
M. Akaki, K. Kimura, Y. Kato, Y. Sawada, Y. Narumi, H. Ohta, T. Kimura, Y. Motome, and M. Hagiwara, Phys. Rev. Research 3, L042043 (2021)
L. Testa, P. Babkevich, Y. Kato, K. Kimura, V. Favre, J. A. Rodriguez-Rivera, J. Ollivier, S. Raymond, T. Kimura, Y. Motome, B. Normand, and H. M. Rønnow, Phys. Rev. B 105, 174413 (2022) [Editors' Suggestion]
こちらも合わせてご覧ください。
加藤康之、木村健太:日本物理学会誌 73, 715 (2018)
Fractional spin fluctuations
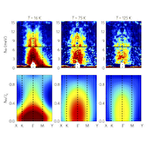
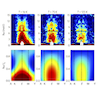
Fractionalization of quantum spins is a prominent feature of quantum spin liquids. Fractional excitations emergent from the fractionalization have their own energy scales depending on types of the quasiparticles. Hence, they are expected to affect the spin dynamics not only in quantum spin liquid states but also paramagnetic states in proximity to the quantum spin liquids. We here compute the spin dynamics at finite temperatures for the Kitaev model, whose ground state is exactly given by quantum spin liquids. Developing and applying new numerical techniques based on a Majorana fermion representation, the cluster extension of dynamical mean-field theory and the continuous-time quantum Monte Carlo method, we clarify the temperature dependences of the dynamical spin structure factor, the NMR relaxation rate, and the magnetic susceptibility. We find unusual behavior never seen in conventional magnets: a dichotomy between static and dynamical spin correlations. It was thus far hard to compute temperature dependences of static quantities. This is the first attempt to our knowledge to systematically study the finite-temperature dynamics of quantum spin liquids.
J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 157203 (2016)
J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 96, 024438 (2017)
J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 96, 064433 (2017)
S.-H. Do, S.-Y. Park, J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, Y. S. Kwon, D. T. Adroja, D. J. Voneshen, K. Kim, T.-H. Jang, J.-H. Park, K.-Y. Choi, and S. Ji, Nature Phys. 13, 1079 (2017)
Y. Nagai, T. Jinno, Y. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, M. Itoh, and Y. Shimizu, Phys. Rev. B 101, 020414(R) (2020)
J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 101, 100408(R) (2020)
J. Nasu and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 104, 045116 (2021) [Editors' Suggestion]
See also
Y. Motome and J. Nasu, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 89, 012002 (2020) [INVITED REVIEW PAPER]
求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 52, 199 (2017); 53, 305 (2018); 54, 217 (2019); 57, 297 (2020)
Fermionic excitations from fractionalization of quantum spins
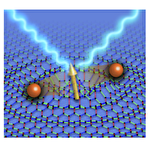
The quantum spin liquid is an exotic quantum disordered state driven by strong quantum fluctuations and many-body effects in insulating magnets. While many candidate materials of this state have been discovered, the theoretical treatment is still controversial; in particular, less is known thus far about finite-temperature properties, which are crucial for critical comparison with experiments. We here study the magnetic Raman scattering spectrum at finite temperatures for the Kitaev model which possesses the exact quantum spin liquid ground state, and compare the results with experiments for a candidate Ru compound. We find that the temperature dependence of the Raman intensity is well described by the Fermi distribution function, reflecting the fact that the fundamental excitations in this system are governed by Majorana fermions emergent from the fractionalization of quantum spins. We show that our result quantitatively agrees with experimental results from about 10K to room temperature, which strongly suggests the existence of emergent Majorana fermions in the real material in this wide temperature range. As the comparison of the Raman intensity is applicable to other candidate materials, it will be widely used as a experimental hallmark of quantum spin liquids.
J. Nasu, J. Knolle, D. L. Kovrizhin, Y. Motome, and R. Moessner, Nature Physics 12, 912 (2016)
Y. Wang, G. B. Osterhoudt, Y. Tian, P. Lampen-Kelley, A. Banerjee, T. Goldstein, J. Yan, J. Knolle, H. Ji, R. J. Cava, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, S. E. Nagler, D. Mandrus, and K. S. Burch, npj Quantum Materials volume 5, 14 (2020)
Press release
See also
Y. Motome and J. Nasu, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 89, 012002 (2020) [INVITED REVIEW PAPER]
求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 52, 199 (2017); 53, 305 (2018); 54, 217 (2019); 57, 297 (2020)
Thermal fractionalization of quantum spins
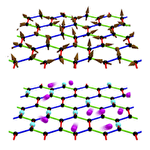
In general, it is hard to prove that a magnet is in a quantum spin liquid state. This is because we need to show the alibi (so-called probatio diabolica), as the quantum spin liquids do not show any symmetry breaking and magnetic ordering down to zero temperature. To avoid the difficulty, a lot of efforts have been made to capture one of prominent features of quantum spin liquids, fractionalization of quantum spins. The spin fractionalization is a phenomenon in which a fundamental degree of freedom, electron spin, is fractionalized into several degrees of freedom. This is regarded as a spin version of charge fractionalization in fractional quantum Hall systems. We here clarify how the spin fractionalization affects thermodynamics, by applying quantum Monte Carlo simulation to the Kitaev model, whose ground state is exactly given by quantum spin liquids. We find that the fractionalized spins release their entropy successively at largely different temperature scales. Our results will be useful for the experimental identification of quantum spin liquids.
J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 92, 115122 (2015)
See also
求 幸年:日本物理学会誌 72, 852 (2017)
Y. Motome and J. Nasu, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 89, 012002 (2020) [INVITED REVIEW PAPER]
求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 52, 199 (2017); 53, 305 (2018); 54, 217 (2019); 57, 297 (2020)
Finite-temperature transition in chiral spin liquids
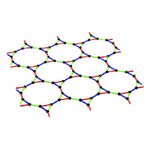
Chiral spin liquids, in which time-reversal symmetry is broken but a long-range magnetic order is absent, have long been studied as a new quantum state of matter. In particular, recently, it has attracted growing interest as the realization of non-Abelian anyons that are useful in fault-tolerant quantum computations. However, less is know how it behaves at finite temperature under thermal fluctuations, although it is important for the quantum computations. By the quantum Monte Carlo simulation, we study the finite-temperature properties of a Kitaev model defined on a decorated-honeycomb lattice, which is know to be a chiral spin liquid at zero temperature. We found that the chiral spin liquid remains robust against thermal fluctuations and it is distinguished from the high-temperature paramagnet by a phase transition. We also clarified that the nature of the phase transition depends on the statistical property of elementary excitations in the chiral spin liquids, anyons. The results pave the way for further understanding of not only quantum magnetism but also quantum computations using non-Abelian anyons.
J. Nasu and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 087203 (2015)
Press release
See also
Y. Motome and J. Nasu, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 89, 012002 (2020) [INVITED REVIEW PAPER]
求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 52, 199 (2017); 53, 305 (2018); 54, 217 (2019); 57, 297 (2020)
Vaporization in quantum spin liquids
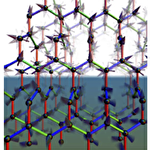
Insulating magnets exhibit paramagnetic behavior with disordered spin directions at high temperature, while magnetic orders with spontaneous symmetry breaking below some critical temperature. The former corresponds to “gas” of quantum spins, and the latter “solid” among the states of matter. In 1973, P. W. Anderson proposed a new quantum state, "quantum spin liquid (QSL)", in which quantum spins are disordered but strongly correlated with each other. This state has been investigated experimentally and theoretically thus far, but its thermodynamic properties have not been revealed yet. In order to solve this problem, we investigate the thermodynamics of a three-dimensional Kitaev model, whose ground state is exactly shown to be a QSL, by newly developing a quantum Monte Carlo simulation on the basis of the Majorana fermion representation. As a result, we discover that a finite-temperature phase transition takes place between the low-temperature QSL and high-temperature paramagnet. We also show that this phase transition is characterized by the change of the topology in the excited states. Our results create a stir in the experimental studies where the adiabatic connection between QSL and paramagnet is implicitly assumed.
J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 197205 (2014)
J. Nasu, T. Kaji, K. Matsuura, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 89, 115125 (2014)
J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 592, 012115 (2015)
Press release
See also
求 幸年:パリティ 30, 10月号 p36 (2015)
求 幸年:パリティ 31, 1月号 p22 (2016)
那須 譲治、宇田川 将文、求 幸年:日本物理学会誌 70, 776 (2015)
求 幸年:日本物理学会誌 72, 852 (2017)
Y. Motome and J. Nasu, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 89, 012002 (2020) [INVITED REVIEW PAPER]
求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 52, 199 (2017); 53, 305 (2018); 54, 217 (2019); 57, 297 (2020)
Unconventional multipole orders and off-diagonal responces induced by hidden antisymmetric spin-orbit coupling
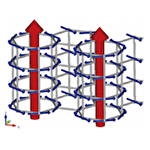
The relativistic spin-orbit coupling in the absence of spatial inversion symmetry has been extensively studied because it leads to various fascinating phenomena, such as unconventional superconductivity and multiferroics. A key concept in these phenomena is the antisymmetric spin-orbit coupling under the inversion symmetry breaking. Recently, it is recognized that a minimal ingredient for the antisymmetric spin-orbit coupling is local parity mixing originating from the inversion symmetry breaking at the lattice sites. We here investigate the influence of the local parity mixing with focusing on itinerant electron systems. As a result, we find that a toroidal ordering, which has been ever discussed only for magnetic insulators, is realized in metallic systems, and induces novel magnetic transport and magnetoelectric effects. Furthermore, we clarify that a spontaneous parity breaking by charge, spin, and orbital ordering activates locally an antisymmetric spin-orbit coupling in the site-dependent form and results in the spin splitting in the band structure and magnetoelectric effect. Our results pave the way for novel electronic ordering, transport, and magnetoelectric phenomena induced by local parity mixing.
S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 90, 024432 (2014) [Editors' Suggestion]
S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 90, 081115(R) (2014)
S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 592, 012101 (2015)
S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 592, 012131 (2015)
S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 84, 064717 (2015)
See also
速水 賢, 楠瀬 博明, 求 幸年:固体物理 50, 217 (2015)
Spin-orbital frustration in pyrochlore molybdenum oxides
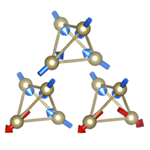
Pyrochlore molybdenum oxides A2Mo2O7 provide a fertile ground for studying metal-insulator transitions and associated unconventional magnetic phenomena. In the insulating materials, a long-range magnetic order is suppressed, and at low temperatures a spin glass behavior appears with frozen magnetic moments in random directions. It has long been believed that the absence of long-range ordering is due to the geometrical frustration between isotropic antiferromgnetic exchnge couplings on the pyrochlore lattice. Recently, however, the neutron scattering experiment for a single crystal of Y2Mo2O7 has revealed an unexpected behavior, that is, the existence of weak ferromagnetic spin fluctuations. This urges reconsideration of the microscopic origin of the spin glass behavior. Performing the state-of-the-art first-principles calculations including the relativistic spin-orbit coupling, we clarified that the ground state suffers from keen competition between antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic states. Furthermore, through the analyses of localized spin model and multi-orbital Hubbard model, we found that the magnetic competition couples with the competition between different orbital orders via the spin-orbit coupling. The new picture of magnetic frustration originating from the orbital degrees of freedom well explains the experimental results.
H. Shinaoka, Y. Motome, T. Miyake, and S. Ishibashi, Phys. Rev. B 88, 174422 (2013) [selected in Kaleidoscope]
See also
H. Shinaoka, Y. Motome, T. Miyake, S. Ishibashi, and P. Werner, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 31, 323001 (2019) [TOPICAL REVIEW]
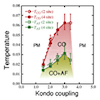
Charge order in Kondo lattice systems
The Kondo lattice model, in which conduction electrons couple with localized quantum spins, is one of the most fundamental models for heavy fermion systems. The model has been intensively studied for searching for novel quantum phases. In particular, the possibility of a charge ordered phase has been examined for more than 30 years, but it was not clarified except for the special cases in one and infinite dimensions. Utilizing two sophisticated numerical methods, a cluster extension of the dynamical mean-field theory and a multi-variables variational Monte Carlo method, we solve this problem and show the evidence of charge ordering in two dimensions. Furthermore, we find that the local Kondo singlet formation plays a key role in stabilizing the charge order. Our results indicate that the charge order in the Kondo lattice systems is qualitatively different from those by intersite Coulomb repulsion. We extend the study to three-dimensional systems, and find that the charge order appears with a noncoplanar magnetic ordering due to the effective frustration under the charge order.
T. Misawa, J. Yoshitake, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 246401 (2013)
S. Hayami, T. Misawa, and Y. Motome, JPS Conf. Proc. 3, 016016 (2014)
Quantum anomalous Hall effect in kagome ice
Spin ice exhibits a peculiar magnetization plateau under the [111] magnetic field. It is considered to be realized by forming a spin liquid state called kagome ice on the [111] kagome planes. For clarifying the effect of the locally-correlated kagome ice on itinerant electrons, we investigate numerically the electronic and transport properties of the spin-ice type Kondo lattice model on a kagome lattice. As a result, we find that the kagome ice spin correlation opens a charge gap in the electronic state in spite of absence of magnetic long-range order. Moreover, the insulating state is a quantum anomalous Hall insulator with a quantization of the Hall conductivity. As increasing magnetic field, the charge gap closes, but opens again in the fully-polarized insulating state, in which the Hall conductivity is quantized at a different value. We show that this is considered as a transition between different topological insulators.
H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 87, 081105(R) (2013)
Dirac half-metal in a triangular ferrimagnet
A monolayer of carbon, graphen, has attracted much interest because of the Dirac electrons with a peculiar linear dispersion in the electronic state. However, it has some difficulty for application to spintronics as the spin-orbit coupling is very weak. We here theoretically propose a possibility of the Dirac electrons from a different point of view. Considering a triangular magnet with itinerant electrons, we show that the Dirac electronic state with a linear dispersion emerges in underlying three-sublattice ferrimagnetic order. The Dirac electrons are perfectly spin-polarized, i.e., the system is half metallic. Furthermore, by Monte Carlo simulation, we clarify the parameter region where the Dirac half-metallic phase is stabilized. The discovery of such new Dirac electrons will stimulate further development of spintronics.
H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 237207 (2012)
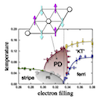
Partial disorder in an Ising-spin Kondo lattice model on a triangular lattice
The triangular-lattice Ising model, a fundamental model for geometrically frustrated systems, exhibits macroscopic degeneracy in the ground state when the interactions are restricted to nearest neighbors and antiferromagnetic. A nontrivial emergent state from this degeneracy is a partial disorder, which is coexistence of magnetic order and paramagnetic moments. In two dimensions, however, the partial disorder is fragile against thermal fluctuations, and does not form a long-range order. Stimulated by recent experimental findings of a partial disorder in quasi-two-dimensional conducting systems, we explore the possibility of partial disorder by the interaction between localized moments and itinerant electrons. By studying an Ising-spin Kondo lattice model on a triangular lattice by Monte Carlo simulation, we found that a partial disorder is stabilized even in two dimensions in the spin-charge coupled system. We clarified that the charge degree of freedom plays a crucial role in the emergence of partial disorder through an electronic phase separation, charge ordering, and opening of the charge gap.
H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 257205 (2012)
H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 87, 155156 (2013)
Hidden multiple-spin interactions in frustrated itinerant-electron systems
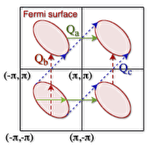
Anomalous Hall effect by spin scalar chiral ordering has attracted much attention. Recently, we found that a four-sublattice noncoplanar chiral order appears near 1/4 filling in one of the fundamental models of frustrated itinerant-electron systems, a Kondo lattice model on a triangular lattice. This state, however, is not explained by the previously-known scenario of the nesting of Fermi surface, and hence, the origin was unclear. We here investigate the stabilization mechanism by carefully examining the perturbation in terms of the spin-charge coupling up to fourth order. As a result, we found that the effective exchange interactions in the second order (RKKY interactions) are degenerate due to the frustration, and that the higher fourth-order contributions play a decisive role. Among many effective multiple-spin interactions in the fourth order, the biquadratic interaction is critically enhanced with a positive coefficient. This is not due to the nesting but a Fermi surface connection, which we call the generalized Kohn anomaly. Our results suggest that the nontrivial stabilization mechanism is hidden in the wide range of frustrated itinerant electron systems.
Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 096401 (2012)
See also
S. Hayami and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 33, 443001 (2021) [TOPICAL REVIEW]
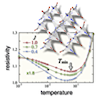
Resistivity minimum in spin-ice conduction systems
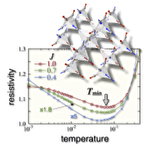
In frustrated magnets called spin ice, a long-range magnetic order is suppressed and a spin-liquid like state can emerge with showing only local spin correlations obeying the so-called ice rule. When such peculiar spatial magnetic texture interacts with itinerant electrons, one can expect some new transport phenomena. We here consider this problem in a model in which spin-ice type Ising moments are coupled with itinerant electrons on a pyrochlore lattice, by employing a cluster extension of the dynamical mean-field theory. As a result, we found that, in low electron density region, the system exhibits a spin-ice like liquid state, and more importantly, the electrical resistivity shows a minimum corresponding to the development of local spin correlations. This clearly shows that the special ice-rule correlation becomes a strong scatterer of electrons, giving a completely new mechanism of resistivity minimum distinct from the conventional Kondo effect. The results suggest the possibility of understanding the resistivity minimum recently observed in some Ir pyrochlore oxides.
M. Udagawa, H. Ishizuka, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 066406 (2012)
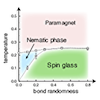
Spin glass transition and spin-lattice coupling in pyrochlore antiferromagnets
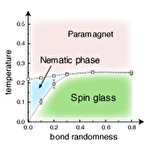
Many frustrated magnets exhibit a spin glass state at low temperatures. Usually the spin glass is induced by randomness, however, in several pyrochlore magnets, a spin glass transition takes place even in a best-quality sample with virtually disorder free, and furthermore, the transition temperature is almost independent of the strength of disorder. To explore the origin of these peculiar behaviors, we investigate the effect of spin-lattice coupling in a bond-disordered pyrochlore Heisenberg antiferromagnet by extensive Monte Carlo simulations. As a result, we find that the spin glass transition temperature is strongly enhanced by the spin-lattice coupling, and remarkably, becomes almost constant in a wide range of the strength of disorder. This is presumably because the spin-lattice coupling enhances the spin collinearity and suppresses thermal fluctuations. The spin glass transition is of second order and its critical properties are compatible with the conventional ones. Our results well account for the puzzling behaviors observed in experiments.
H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 047204 (2011)
H. Shinaoka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 82, 134420 (2010)
H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 320, 012009 (2011)
H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 400, 032087 (2012)
H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 90, 165119 (2014)
See also
品岡 寛、富田 裕介、求 幸年:日本物理学会誌 67, 762 (2012)
Spin scalar chirality ordering and anomalous Hall effect in triangular-lattice ferromagnetic Kondo models
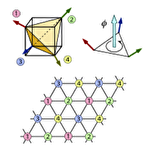
Recently, spin scalar chirality has attracted much attention as a novel origin of the anomalous Hall effect (AHE), independent of the relativistic spin-orbit coupling. In fact, it was pointed out that AHE is induced by noncoplanar magnetic orders on the kagome or triangluar lattice. However, in the previous studies, such magnetic orders were given by hand with neglecting effects of itinerant electrons, and their stability relative to other orders was not examined. In the present study, we investigate the ground state of the ferromagnetic Kondo model on the triangular lattice by variational calculations for various magnetic states up to four-sublattice orders. As a result, we find that a four-sublattice scalar chiral order emerges around 1/4 filling, in addition to 3/4 filling which was predicted previously. The 1/4 filling phase is stable in a wider range of parameters than the nesting-driven 3/4 filling one. We also compute the Hall conductivity in these chiral phases, which is quantized according to the Chern number in gapped insulating states.
Y. Akagi and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 79, 083711 (2010) [The 25th Outstanding Paper Award of the Physical Society of Japan]
Y. Akagi and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 320, 012059 (2011)
See also
S. Hayami and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 33, 443001 (2021) [TOPICAL REVIEW]
Partial Kondo screening in frustrated Kondo lattice systems
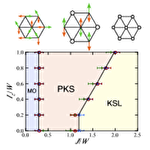
One of the most important concepts in Kondo lattice systems is competition between the Kondo coupling and the RKKY interaction. The competition leads to a quantum critical point (QCP) between a magnetically-ordered state and a Fermi liquid state, and furthermore, it is the origin of novel phenomena around the QCP, such as a non-Fermi liquid behavior and a superconductivity. To explore a new quantum phase related to the competition, we investigate the ground state of geometrically-frustrated Kondo lattice systems by employing a high-precision variational Monte Carlo simulation. We find that a partially-ordered state, in which a magnetic order and a Kondo spin singlet coexists, emerges between a magnetically-ordered state stabilized by the RKKY interaction and a Kondo spin liquid state stabilized by the Kondo coupling. We clarified that this new quantum phase is stabilized by quantum fluctuations as well as magnetic anisotropy, and that it is accompanied by a charge disproportionation.
Y. Motome, K. Nakamikawa, Y. Yamaji, and M. Udagawa, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 036403 (2010)
Y. Motome, Y. Yamaji, and M. Udagawa, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 145, 012068 (2009)
Y. Motome, K. Nakamikawa, Y. Yamaji, and M. Udagawa, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80, Suppl. A, SA133 (2011)
Member
Please replace '(at)' by '@', 'ap' by 'ap.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp', 'aion' by 'aion.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp', 'ecc' by 'g.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp'.
| Faculties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yukitoshi MOTOME | Professor | motome(at)ap tel: +81-3-5841-6815 fax: +81-3-5841-8897 | room 225 | Scopus cv |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kotaro SHIMIZU | Research Associate | shimizu(at)ap tel/fax: +81-3-5841-6817 | room 226 | Scopus
web page |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natsuko KAWAMATA | Secretary | n-kawamata(at)ecc tel: +81-3-5841-6817 | room 226 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PostDocs | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Manodip ROUTH | routh-manodip(at)ecc | room 218 | Scopus |
| Students | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motoki AMANO | Doctor course | amano-motoki803(at)ecc | room 218 | |
| Takuma OGIHARA | Doctor course | takumaogi766(at)ecc | room 214 | |
| Kaito KOBAYASHI | Doctor course | kaito-kobayashi92(at)ecc | room 228 | web page |
| Lingzhi ZHANG | Doctor course | lingzhi(at)ecc | room 214 | |
| Seongjun KWON | Doctor course | sjkwon(at)ecc | room 218 | |
| Midori YAMADA | Doctor course | midori-yamada(at)ecc | room 228 | |
| Shoya KASAI | Docter course | kasai(at)aion | room 220 | |
| Atsuro ARAI | Master course | atsuar4421(at)ecc | room 226 | |
| Sogen IKEGAMI | Master course | ikegami-sogen443(at)ecc | room 218 | web page |
| Aoi KAJIHARA | Master course | a.kajihara(at)aion | room 226 | |
| Joseph LAURIENZO | Master course | laurienzo(at)ecc | room 220 | |
| Former Members (click to show/hide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Project
| Ongoing projects | ||
|---|---|---|
| Exploring quantum emergence through correlation design science | Grant-in-Aid for Transformative Research Areas (A) (2025〜2029) ) web page | Project leader: Ryotaro Arita (Univ. of Tokyo) |
| Creation and control of functional magnetic materials based on multi-scale computational materials science | Grant-in-Aid for Research Activity Start-up (2024〜2025) | Project leader: Kotaro Shimizu |
| Completed projects (click to show/hide) |
|
|---|
Outcome
Research highlightPublications (click to show/hide)
- Y. Tokura, Y. Motome, and K. Ueda, Rep. Prog. Phys. 88, 056001 (2025), "Metal-insulator transitions in pyrochlore oxides"
- 求 幸年:第69回物性若手夏の学校 講義テキスト "スピン液体の物理"
- M. Naka, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, npj Spintronics 3, 1 (2025), "Altermagnetic perovskites"
- 中 惇、求 幸年、妹尾仁嗣:固体物理 59, 241 (2024), "交替磁性体のスピン分裂と交差相関"
- 求 幸年:月刊 研究開発リーダー 2023年8月号, "自動微分を用いた数理モデルの最適化と物質・材料の自動設計"
- 清水宏太郎、奥村駿、加藤康之、求 幸年:日本物理学会誌 78, 314 (2023), "トポロジカル磁気構造におけるスピンモアレエンジニアリング"
- 張 成燻、求 幸年:固体物理 57, 757 (2022), "キタエフスピン液体の物質設計"
- 固体物理特集号 57, 613-784 (2022), "キタエフスピン液体の新展開" (編集委員:芝内孝禎・遠山貴巳・求 幸年)
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 33, 443001 (2021), "Topological spin crystals by itinerant frustration" [TOPICAL REVIEW]
- 紺谷 浩、求 幸年:日本液晶学会誌「液晶」25, 168 (2021), "量子液晶の理論的研究"
- 東京大学物性研究所スーパーコンピュータセンター パンフレット (2021年3月発行), "研究ハイライト:磁石に潜むマヨラナ粒子"
- Y. Motome, R. Sano, S.-H. Jang, Y. Sugita, and Y. Kato, J. Phys: Condens. Matter 32, 404001 (2020), "Materials design of Kitaev spin liquids beyond the Jackeli-Khaliullin mechanism" [Special Issue on Quantum Spin Liquids]
- Y. Motome and J. Nasu, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 89, 012002 (2020), "Hunting Majorana Fermions in Kitaev Magnets" [INVITED REVIEW PAPER]
- 求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 55, 297 (2020), "量子スピン液体研究の最前線(その4: 最終回)"
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Motome, T. Miyake, S. Ishibashi, and P. Werner, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 31, 323001 (2019), "First-principles studies of spin-orbital physics in pyrochlore oxides" [TOPICAL REVIEW]
- 求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 54, 217 (2019), "量子スピン液体研究の最前線(その3)"
- 加藤康之、木村健太:日本物理学会誌 73, 715 (2018), "正四角台塔をユニットに持つ反強磁性体が示す電気磁気効果"
- 求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 53, 305 (2018), "量子スピン液体研究の最前線(その2)"
- 求 幸年:日本物理学会誌 72, 852 (2017), "分裂するスピン"
- 小澤 遼:academist Journal (2017年8月8日), "高いトポロジカル数をもつ磁気スキルミオンを発見 - 超小型メモリデバイスの開発に向けて"
- 求 幸年、那須 譲治:固体物理 52, 199 (2017), "量子スピン液体研究の最前線(その1)"
- 求 幸年:パリティ 31, 1月号 p22 (2016), "計算機で見る磁性体の新しい相転移"
- 那須 譲治、宇田川 将文、求 幸年:日本物理学会誌 70, 776 (2015), "キタエフ量子スピン液体の"気液"相転移"
- 求 幸年:パリティ 30, 10月号 p36 (2015), "量子スピン液体を計算機で温める:新しい磁気相転移の発見"
- 速水 賢、楠瀬 博明、求 幸年:固体物理 50, 217 (2015), "遍歴電子系における自発的な空間反転対称性の破れ ー非従来型多極子秩序とスピン・バレー分裂、非対角応答ー"
- 那須 譲治、宇田川 将文、求 幸年:セラミックス協会誌「セラミックス」2015年5月号トピックス, "量子スピン液体と常磁性状態の間に現れる有限温度相転移"
- 品岡 寛、富田 裕介、求 幸年:日本物理学会誌 67, 762 (2012), "幾何学的フラストレーションとスピン格子結合から生じる新しいスピングラス挙動"
- 宇田川 将文、石塚 大晃、求 幸年:固体物理 46, 87 (2011), "アイスルール伝導系の量子臨界挙動と分数電荷励起"
- 求 幸年:パリティ 25, 5月号 p68 (2010), "フラストレーションが結ぶ諸自由度 — スピン、格子、軌道、電荷"
- 求 幸年:物性研究 89, 863 (2008), "遍歴と局在のはざ間でせめぎ合う電荷・スピン・軌道自由度"
- 求 幸年, 宮坂 茂樹:固体物理 38, 629 (2003), "ペロフスカイトバナジウム酸化物のスピン軌道物性"
- 日本経済新聞 (2025年10月23日付), "理研と東大など、p波磁性体と呼ばれる新しいタイプの磁性体を実現"
- 東京大学大学院工学系研究科 プレスリリース, "p波磁性体と呼ばれる新しいタイプの磁性体を実現-電流を用いた高効率な磁化制御などへ期待-" [詳細]
- 日本経済新聞 (2025年4月25日付), "東大、量子多体系の情報処理性能を通じて相転移現象を解明"
- Press Release, "Exploring Quantum Phase Transitions Through the Lens of Quantum Reservoir Probing"
- 日本経済新聞 (2025年3月6日付), "福井大・東北大・千葉大・東大・スピン流が量子スピン液体を応用したトポロジカル量子計算の鍵となる可能性を開拓"
- Press Release, "Capturing Majorana Particles with Spintronics"
- マイナビニュース (2023年10月13日付), "東大、物理リザバーコンピューティングの課題を解決する動作原理を発見"
- Press Release, "Thermally-robust spatiotemporal parallel reservoir computing by frequency filtering in frustrated magnets"
- 日刊工業新聞 (2023年10月11日付), "東大、極低温で超大規模並列計算 磁性体電子使い新手法"
- 日本経済新聞 (2023年10月10日付), "東大、電子のスピンを用いた人工ニューラルネットワークの新しい動作原理を発見"
- 月刊 研究開発リーダー 2023年8月号, "自動微分を用いた数理モデルの最適化と物質・材料の自動設計"
- 日本経済新聞 (2023年6月13日付), "東北大・東大・高エネ研・JST、バンドトポロジーの性質をアモルファス薄膜で発見"
- Press Release, "Berry curvature contributions of kagome-lattice fragments in amorphous Fe–Sn thin films"
- 日刊工業新聞 (2023年3月8日付), "経営ひと言/東京大学・求幸年教授「データ不要」"
- 日刊工業新聞 (2023年3月2日付), "数理モデルから欲しい結果逆算 東大・理研が新手法、自動微分で変数最適化"
- 日本経済新聞 (2023年3月1日付), "東大と理研、狙った物性を示す物質を自動設計する理論手法を開発"
- Press Release, "Inverse Hamiltonian design by automatic differentiation"
- 日本経済新聞 (2021年12月24日付), "神戸大・阪大・東大、交流電場を用いた新規測定技術によりテラヘルツ電磁波の非相反線二色性の観測に成功"
- Press Release, "Nonreciprocal linear dichroism observed in electron spin resonance spectra of the magnetoelectric multiferroic Pb(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4"
- 日刊工業新聞 (2021年12月2日付), "磁気渦結晶に新パターン 東大、トポロジカルスピン結晶で発見"
- Press Release, "Phase shift in skyrmion crystals"
- 日刊工業新聞 (2021年8月5日付), "京大など、「非可換エニオン」性質解明 量子コンピューター実現へ"
- 日経XTECH (2021年8月2日付), "ノイズに強いトポロジカル量子コンピューター、京大・JSTなどが有力な候補粒子を解明"
- Press Release, "Half-integer quantized anomalous thermal Hall effect in the Kitaev material candidate α-RuCl3 : Professor Yukitoshi Motome, Department of Applied Physics, and other researchers."
- 日本経済新聞 (2020年11月23日付), "理研と東大、ナノメートルサイズの磁気渦構造が伝導電子に現れることを発見"
- Press Release, "Imaging the coupling between itinerant electrons and localised moments in the centrosymmetric skyrmion magnet GdRu2Si2" [詳細]
- 日本経済新聞 (2020年5月18日付), "東大・広島大・阪大、電荷密度波を形成するVTe2の電子構造の解明に成功"
- Press Release, "Switching of band inversion and topological surface states by charge density wave"
- 日本経済新聞 (2019年9月20日付), "早大・北大・明大・東北大・東大など、水素や炭素などのありふれた原子からなる有機化合物を使った新しいスピン流生成機構を発見"
- Press Release, "Spin current generation in organic antiferromagnets"
- NHK (2018年7月12日付), "「マヨラナ粒子」の存在を証明"
- 共同通信 (2018年7月12日付), "「幻の粒子・マヨラナ」存在か?量子コンピューター、京大が実験"
- 日刊工業新聞 (2018年7月12日付), "幻の「マヨラナ粒子」の存在を実証、量子コンピューターの進化に期待 京大、東大、東工大の研究チーム"
- 毎日新聞 (2018年7月12日付), "マヨラナ粒子 京大グループが実証 同じ動きを観測"
- 毎日新聞 (2018年7月12日付), "マヨラナ粒子 実証 同じ動きを観測 京大グループ"
- 日本経済新聞 (2018年7月12日付), "「幻の粒子」京大など発見 予言から80年、量子計算機に応用も"
- 日本経済新聞 (2018年7月12日付), "京大・東大・東工大、幻の粒子「マヨラナ粒子」を実証することに成功 ートポロジカル量子コンピューター実現に期待"
- 朝日新聞 (2018年7月12日付), "予言から80年、幻の「マヨラナ粒子」確認 京都大など"
- Press Release, "Majorana quantization and half-integer thermal quantum Hall effect in a Kitaev spin liquid"
- 日本経済新聞 (2017年4月3日付), "東大、高いトポロジカル数をもつ磁気スキルミオンを発見"
- 日経テクノロジーonline (2017年4月4日付), "多段スイッチングを可能とする磁気スキルミオン"
- 日刊工業新聞 (2017年4月4日付), "東大、トポロジカル数持つ渦状スピン磁性体を発見"
- Press Release, "Zero-Field Skyrmions with a High Topological Number in Itinerant Magnets"
- 日刊工業新聞 (2016年7月15日付), "東工大と東大、幻の「マヨラナ粒子」の創発を発見ー室温磁性絶縁体中で"
- 科学新聞 (2016年7月15日付), "マヨラナ粒子の創発ー磁性絶縁体中で捉える"
- Press Release, "Fermionic response from fractionalization in an insulating two-dimensional magnet"
- 化学工業日報 (2016年7月5日付), "東工大-東大 「マヨナラ粒子」の創発 磁性絶縁体中で捕捉"
- 科学新聞 (2015年9月14日付), "カイラルスピン液体状態が熱揺らぎに対し安定に存在"
- Press Release, "Thermodynamics of Chiral Spin Liquids with Abelian and Non-Abelian Anyons"
- Press Release, "Novel spin gas-liquid transition in quantum magnets -Unveiling a new phase transition by large-scale numerical simulationsー"
- 日刊工業新聞 (2014年11月6日付), "量子スピン液体と常磁性状態の間には相転移が常に存在ー東大・東工大が発見"
- マイナビニュース (2014年10月30日付), "東工大と東大、大規模数値計算により新しい相転移現象を発見"
- 特願 2023-025883「情報処理システム、情報処理方法およびプログラム」求 幸年、小林海翔(2023年2月22日出願)
- S. Okumura, M. M. Moritz, and Y. Motome, preprint (arXiv:2512.14071), "Spiral-induced Anomalous Hall Effect from Odd-parity Spin-nodal Lines"
- S. Ikegami, K. Fukui, R. Pohle, and Y. Motome, preprint (arXiv:2512.06322), "Kitaev Meets AKLT: Competing Quantum Disorder in Spin-3/2 Honeycomb Systems"
- S. Kasai, S. Okumura, and Y. Motome, preprint (arXiv:2511.23045), "Nonequilibrium dynamics of magnetic hopfions driven by spin-orbit torque"
- S. Kasai, S. Okumura, and Y. Motome, preprint (arXiv:2511.23027), "Controlling Knot Topology in Magnetic Hopfions via Spin-orbit Torque"
- Y. Kato, T. Hayashida, K. Matsumoto, T. Kimura, and Y. Motome, preprint (arXiv:2511.22801), "Electric-field-induced magnetic toroidal moment and nonlinear magnetoelectric effect in antiferromagnetic olivines"
- S. Ikegami, K. Fukui, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, preprint (arXiv:2511.14134), "Topological transition induced by selective random defects on a honeycomb lattice"
- C. Ojeda-Aristizabal, X. Zheng, C. Xu, Z. Nussinov, Y. Motome, A. Banerjee, A. W. Tsen, M. Knap, R.-R. Du, G. Joshi, A. Mounce, Y. Kim, B. M. Hunt, D. Shcherbakov, B. Zhou, R. Jing, M. Liu, H. Zhao, B. Liao, M. Claassen, O. Erten, Y. P. Chen, and E. A. Henriksen, preprint (arXiv:2511.13838), "Lessons from α-RuCl3 for pursuing quantum spin liquid physics in atomically thin materials"
- R. Pohle, Y. Motome, T. Tadano, and S. Hoshino, preprint (arXiv:2507.19764), "Electron-phonon coupled Langevin dynamics for Mott insulators"
- T. Okubo, J. Nasu, T. Misawa, and Y. Motome, preprint (arXiv:2507.16558), "Thermal Hall transport in Kitaev spin liquids"
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Motome, preprint (arXiv:2506.17547), "Edge of Many-Body Quantum Chaos in Quantum Reservoir Computing"
- Y.-F. Zhao, S.-H. Jang, and Y. Motome, preprint (arXiv:2403.09112), "Spin-Orbit Coupled Insulators and Metals on the Verge of Kitaev Spin Liquids in Ilmenite Heterostructures"
- S. Wadashima and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 112, 214204 (2025), "Spin-liquid and spin-glass behavior in quantum spin models with all-to-all p-spin interactions"
- S. Kasai, K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 112, 184424 (2025), "Three-dimensional topological superstructure of magnetic hopfions threaded by meron strings in easy-plane magnets"
- R. Yamada, M. T. Birch, P. R. Baral, S. Okumura, R. Nakano, S. Gao, M. Ezawa, T. Nomoto, J. Masell, Y. Ishihara, K. K. Kolincio, I. Belopolski, H. Sagayama, H. Nakao, K. Ohishi, T. Ohhara, R. Kitanagi, T. Nakajima, Y. Tokura, T. Arima, Y. Motome, M. M. Hirschmann, and M. Hirschberger, Nature 646, 837 (2025), "A metallic p-wave magnet with commensurate spin helix"
- K. Fukui and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 112, 14411 (2025), "Topological Majorana flat bands in the Kitaev model on a Bishamon-kikko lattice"
- Y. Ihara, T. Kanda, K. Matsui, K. Kindo, Y. Kohama, Y. Kato, Y. Motome, T. Kimura, and K. Kimura, Phys. Rev. B 112, 094405 (2025), "High-field NMR study of field-induced states in Pb(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4"
- M. Negishi, K. Fujiwara, S.-H. Jang, Y.-F. Zhao, S. Sasano, R. Ishikawa, N. Shibata, D. Shiga, H. Kumigashira, Y. Nakamura, H. Kishida, Y. Motome, and A. Tsukazaki, Phys. Rev. Materials 9, 086202 (2025), "Mott insulating state of IrO6 honeycomb monolayer structured in ilmenite-type oxide superlattice"
- M. Naka, Y. Motome, T. Miyazaki, and H. Seo, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 94, 083702 (2025), "Nonrelativistic Piezomagnetic Effect in an Organic Altermagnet" [Editors' Choice]
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Motome, SciPost Phys. 18, 198 (2025), "Quantum reservoir probing: An inverse paradigm of quantum reservoir computing for exploring quantum many-body physics"
- Y. Tokura, Y. Motome, and K. Ueda, Rep. Prog. Phys. 88, 056001 (2025), "Metal-insulator transitions in pyrochlore oxides"
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Motome, Nat. Commun. 16, 3871 (2025), "Quantum reservoir probing of quantum phase transitions"
- Y. Kato, J. Nasu, M. Sato, T. Okubo, T. Misawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. X 15, 011050 (2025), "Spin Seebeck Effect as a Probe for Majorana Fermions in Kitaev Spin Liquids"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Commun. Phys. 8, 69 (2025), "Current-induced motion of nanoscale magnetic torons over the wide range of the Hall angle"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 111, 024411 (2025), "Soliton penetration from edges in a monoaxial chiral magnet"
- M. Naka, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, npj Spintronics 3, 1 (2025), "Altermagnetic perovskites"
- L. Zhang and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 110, L241109 (2024), "Possible realization of Kitaev spin liquids in van der Waals heterostructures of α-RuCl3 and CrX3 (X=Cl and I)"
- Y. Fujishiro, C. Terakura, A. Miyake, N. Kanazawa, K. Nakazawa, N. Ogawa, H. Kadobayashi, S. Kawaguchi, T. Kagayama, M. Tokunaga, Y. Kato, Y. Motome, K. Shimizu, and Y. Tokura, Phys. Rev. B 110, L220401 (2024), "Pressure-induced quantum melting of chiral spin order and subsequent transition to a degenerate semiconductor state in FeGe" [Editors' Suggestion]
- S. Ikegami, K. Fukui, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 110, 245107 (2024), "Topological phase diagram of the Haldane model on a Bishamon-kikko–honeycomb lattice"
- S.-H. Jang and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 110, 155124 (2024), "Exchange interactions in rare-earth magnets A2PrO3 (A= alkali metals)"
- S.-H. Jang and Y. Motome, Commun. Mater. 5, 192 (2024), "Exploring rare-earth Kitaev magnets by massive-scale computational analysis"
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 110, 085112 (2024), "Topological transitions by magnetization rotation in kagome monolayers of the ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal Co-based shandite"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 110, 024429 (2024), "Magnetic field effects on the Kitaev model coupled to environment"
- R. Pohle, N. Shannon, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Research 6, 033077 (2024), "Eight-color chiral spin liquid in the S=1 bilinear-biquadratic model with Kitaev interactions"
- K. Inui and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Research 6, 033080 (2024),"Inverse Hamiltonian design of highly-entangled quantum systems"
- J. Spethmann, N. D. Khanh, H. Yoshimochi, R. Takagi, S. Hayami, Y. Motome, R. Wiesendanger, S. Seki, and K. von Bergmann, Phys. Rev. Materials 8, 064404 (2024), "SP-STM study of the multi-Q phases in GdRu2Si2"
- N. Mitsuishi, Y. Sugita, T. Akiba, Y. Takahashi, M. Sakano, K. Horiba, H. Kumigashira, H. Takahashi, S. Ishiwata, Y. Motome, and K. Ishizaka, Phys. Rev. Research 6, 013155 (2024), "Unveiling the orbital-selective electronic band reconstruction through the structural phase transition in TaTe2"
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Commun. Phys. 7, 48 (2024), "Magnetic, transport and topological properties of Co-based shandite thin films"
- S.-H. Jang and Y. Motome, AIP Advances 14, 015229 (2024), "Metallic ruthenium ilmenites: First-principles study of MgRuO3 and CdRuO3"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 108, 134436 (2023), "Emergent electric field from magnetic resonances in a one-dimensional chiral magnet"
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Motome, Sci. Rep. 13, 15123 (2023), "Thermally-robust spatiotemporal parallel reservoir computing by frequency filtering in frustrated magnets"
- T. Misawa, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 108, 115117 (2023), "Interedge spin resonance in the Kitaev quantum spin liquid"
- T. Nomura, Y. Kato, Y. Motome, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, Y. Kohama, S. Zherlitsyn, J. Wosnitza, S. Kimura, T. Katsuyoshi, T. Kimura, and K. Kimura, Phys. Rev. B 108, 054434 (2023), "High-field phase diagram of the chiral-lattice antiferromagnet Sr(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4"
- K. Fujiwara, Y. Kato, H. Abe, S. Noguchi, J. Shiogai, Y. Niwa, H. Kumigashira, Y. Motome, and A. Tsukazaki , Nat. Commun. 14, 3399 (2023), "Berry curvature contributions of kagome-lattice fragments in amorphous Fe–Sn thin films"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 92, 064708 (2023), "Ground-State Phase Diagram of the Kitaev–Heisenberg Model on a Three-dimensional Hyperhoneycomb Lattice"
- R. Pohle, N. Shannon, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 107, L140403 (2023), "Spin nematics meet spin liquids: Exotic quantum phases in the spin-1 bilinear-biquadratic model with Kitaev interactions"
- Y. Kato and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 107, 094437 (2023), "Hidden topological transitions in emergent magnetic monopole lattices"
- K. Inui and Y. Motome, Commun. Phys. 6, 37 (2023), "Inverse Hamiltonian design by automatic differentiation"
- M. Naka, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, Phys Rev. B 106, 195149 (2022), "Anomalous Hall effect in antiferromagnetic perovskites"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 106, 174416 (2022), "Ground-state phase diagram of spin-S Kitaev-Heisenberg models"
- S. Suetsugu, Y. Ukai, M. Shimomura, M. Kamimura, T. Asaba, Y. Kasahara, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, T. Shibauchi, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, and Y. Matsuda, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 91, 124703 (2022), "Evidence for a Phase Transition in the Quantum Spin Liquid State of a Kitaev Candidate α-RuCl3"
- S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 91, 093702 (2022), "Magnetic Hedgehog Lattice in a Centrosymmetric Cubic Metal"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 106, 014419 (2022), "Feasibility of Kitaev quantum spin liquids in ultracold polar molecules"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 105, 224405 (2022), "Phase degree of freedom and topology in multiple-Q spin textures"
- L. Testa, P. Babkevich, Y. Kato, K. Kimura, V. Favre, J. A. Rodriguez-Rivera, J. Ollivier, S. Raymond, T. Kimura, Y. Motome, B. Normand, and H. M. Rønnow, Phys. Rev. B 105, 174413 (2022), "Spin dynamics in the square-lattice cupola system Ba(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4" [Editors' Suggestion]
- Y. Kato and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 105, 174413 (2022), "Magnetic field–temperature phase diagrams for multiple-Q magnetic ordering: Exact steepest descent approach to long-range interacting spin systems"
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 105, 165152 (2022), "Asymmetric modulation of Majorana excitation spectra and nonreciprocal thermal transport in the Kitaev spin liquid under a staggered magnetic field"
- Y. Motome, JPSJ News Comments 19, 04 (2022), "Toward a Deeper Insight into Nonlinear Response"
- N. D. Khanh, T. Nakajima, S. Hayami, S. Gao, Y. Yamasaki, H. Sagayama, H. Nakao, R. Takagi, Y. Motome, Y. Tokura, T. Arima, and S. Seki, Adv. Sci. 9, 2105452 (2022), "Zoology of Multiple-Q Spin Textures in a Centrosymmetric Tetragonal Magnet with Itinerant Electrons"
- M. Akaki, K. Kimura, Y. Kato, Y. Sawada, Y. Narumi, H. Ohta, T. Kimura, Y. Motome, and M. Hagiwara, Phys. Rev. Research 3, L042043 (2021), "Nonreciprocal linear dichroism observed in electron spin resonance spectra of the magnetoelectric multiferroic Pb(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4"
- Y. Kato, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 104, 224405 (2021), "Spin excitation spectra in helimagnetic states: Proper-screw, cycloid, vortex-crystal, and hedgehog lattices"
- S. Hayami, T. Okubo, and Y. Motome, Nat. Commun. 12, 6927 (2021), "Phase shift in skyrmion crystals"
- K. Inui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Research 3, 043126 (2021), "Determinant-free fermionic wave function using feed-forward neural networks"
- S. Okumura, T. Morimoto, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 104, L180407 (2021), "Quadratic optical responses in a chiral magnet", Erratum, ibid. 104, 219902 (2023)
- K. Fujiwara, Y. Kato, T. Seki, K. Nomura, K. Takanashi, Y. Motome, and A. Tsukazaki , Commun. Mater. 2, 113 (2021), "Tuning scalar spin chirality in ultrathin films of the kagome-lattice ferromagnet Fe3Sn"
- T. Katsuyoshi, K. Kimura, Z. Yang, Y. Kato, S. Kimura, Y. Motome, Y. Kohama, and T. Kimura, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 90, 123701 (2021), "Nonreciprocal Directional Dichroism in a Magnetic-Field-Induced Ferroelectric Phase of Pb(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4" [Papers of Editors' Choice]
- S.-H. Jang and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Materials 5, 104409 (2021), "Electronic and magnetic properties of iridium ilmenites AIrO3 (A= Mg, Zn, and Mn)"
- P. A. Mishchenko, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. D 104, 074517 (2021), "Quantum Monte Carlo method on asymptotic Lefschetz thimbles for quantum spin systems: An application to the Kitaev model in a magnetic field"
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 104, 144404 (2021), "Charge density waves in multiple-Q spin states"
- S.-H. Jang, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 104, 085142 (2021), "Vortex creation and control in the Kitaev spin liquid by local bond modulations"
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 33, 443001 (2021), "Topological spin crystals by itinerant frustration" [TOPICAL REVIEW]
- T. Yokoi, S. Ma, Y. Kasahara, S. Kasahara, T. Shibauchi, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, C. Hickey, S. Trebst, and Y. Matsuda, Science 373, 568 (2021), "Half-integer quantized anomalous thermal Hall effect in the Kitaev material candidate α-RuCl3"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 104, 045116 (2021), "Spin dynamics in the Kitaev model with disorder: Quantum Monte Carlo study of dynamical spin structure factor, magnetic susceptibility, and NMR relaxation rate" [Editors' Suggestion]
- K. Kimura, Y. Kato, S. Kimura, Y. Motome, and T. Kimura, npj Quantum Mater. 6, 54 (2021), "Crystal-chirality-dependent control of magnetic domains in a time-reversal-broken antiferromagnet"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 103, 184421 (2021), "Spin moire engineering of topological magnetism and emergent electromagnetic fields"
- H. Watanabe, Y. Kato, H. C. Po, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 103, 134430 (2021), "Fractional corner magnetization of collinear antiferromagnets"
- M. Naka, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, Phys. Rev. B 103, 125114 (2021), "Perovskite as a spin current generator"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 103, 054427 (2021), "Phase transitions between helices, vortices, and hedgehogs driven by spatial anisotropy in chiral magnets"
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 103, 054422 (2021), "Noncoplanar multiple-Q spin textures by itinerant frustration: Effects of single-ion anisotropy and bond-dependent anisotropy"
- T. Sato, Y. Umimoto, Y. Sugita, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 103, 054416 (2021), "Optical Hall response in spin-orbit coupled metals: Comparative study of magnetic cluster monopole, quadrupole, and toroidal orders"
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 103, 024439 (2021), "Square skyrmion crystal in centrosymmetric itinerant magnets"
- Y. Yasui, C. J. Butler, N. D. Khanh, S. Hayami, T. Nomoto, T. Hanaguri, Y. Motome, R. Arita, T. Arima, Y. Tokura, and S. Seki, Nature Communications 11, 5925 (2020), "Imaging the coupling between itinerant electrons and localised moments in the centrosymmetric skyrmion magnet GdRu2Si2"
- S.-H. Jang, R. Sano, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Materials 4, 104420 (2020), "Computational design of f-electron Kitaev magnets: Honeycomb and hyperhoneycomb compounds A2PrO3 (A= alkali metals)"
- K. Inui and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 102, 155126 (2020), "Channel-selective non-Fermi liquid behavior in the two-channel Kondo lattice model under a magnetic field", Erratum, ibid. 105, 239901 (2022)
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 102, 054437 (2020), "Thermodynamic and transport properties in disordered Kitaev models"
- T. Eschmann, P. A. Mishchenko, K. O'Brien, T. A. Bojesen, Y. Kato, M. Hermanns, Y. Motome, and S. Trebst, Phys. Rev. B 102, 075125 (2020), "Thermodynamic classification of three-dimensional Kitaev spin liquids"
- M. Naka, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, Y. Yanagi, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, Phys. Rev. B 102, 075112 (2020), "Anomalous Hall effect in κ-type organic antiferromagnets"
- Y. Motome, R. Sano, S.-H. Jang, Y. Sugita, and Y. Kato, J. Phys: Condens. Matter 32, 404001 (2020), "Materials design of Kitaev spin liquids beyond the Jackeli-Khaliullin mechanism" [Special Issue on Quantum Spin Liquids]
- M. Onga, Y. Sugita, T. Ideue, Y. Nakagawa, R. Suzuki, Y. Motome, and Y. Iwasa, Nano Letters 20, 4625 (2020), "Antiferromagnet-Semiconductor Van Der Waals Heterostructures: Interlayer Interplay of Exciton with Magnetic Ordering"
- N. Mitsuishi, Y. Sugita, M. S. Bahramy, M. Kamitani, T. Sonobe, M. Sakano, T. Shimojima, H. Takahashi, H. Sakai, K. Horiba, H. Kumigashira, K. Taguchi, K. Miyamoto, T. Okuda, S. Ishiwata, Y. Motome, and K. Ishizaka, Nat. Commun. 11, 2466 (2020), "Switching of band inversion and topological surface states by charge density wave" [selected as FOCUS]
- S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 101, 144416 (2020), "Magnetic hedgehog lattices in noncentrosymmetric metals"
- Y. Sugita, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 101, 100410(R) (2020), "Antiferromagnetic Kitaev interactions in polar spin-orbit Mott insulators"
- J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 101, 100408(R) (2020), "Majorana-magnon crossover by a magnetic field in the Kitaev model: Continuous-time quantum Monte Carlo study"
- Y. Wang, G. B. Osterhoudt, Y. Tian, P. Lampen-Kelley, A. Banerjee, T. Goldstein, J. Yan, J. Knolle, H. Ji, R. J. Cava, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, S. E. Nagler, D. Mandrus, and K. S. Burch, npj Quant. Mat. 5, 14 (2020), "The range of non-Kitaev terms and fractional particles in α-RuCl3"
- Y. Nagai, T. Jinno, Y. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, M. Itoh, and Y. Shimizu, Phys. Rev. B 101, 020414(R) (2020), "Two-step gap opening across the quantum critical point in the Kitaev honeycomb magnet α-RuCl3"
- P. A. Mishchenko, Y. Kato, K. O'Brien, T. A. Bojesen, T. Eschmann, M. Hermanns, S. Trebst, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 101, 045118 (2020), "Chiral spin liquids with crystalline Z2 gauge order in a three-dimensional Kitaev model" [Editors' Suggestion]
- Y. Motome and J. Nasu, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 89, 012002 (2020), "Hunting Majorana Fermions in Kitaev Magnets" [INVITED REVIEW PAPER]
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Research 1, 033007 (2019), "Nonequilibrium Majorana dynamics by quenching a magnetic field in Kitaev spin liquids"
- T. Eschmann, P. A. Mishchenko, T. A. Bojesen, Y. Kato, M. Hermanns, Y. Motome, and S. Trebst, Phys. Rev. Research 1, 032011(R) (2019), "Thermodynamics of a gauge-frustrated Kitaev spin liquid"
- M. Naka, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, Y. Yanagi, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, Nat. Commun. 10, 4305 (2019), "Spin current generation in organic antiferromagnets" [Editors’ Highlights]
- L. Rossi, A. Bobel, S. Wiedmann, R. Kuchler, Y. Motome, K. Penc, N. Shannon, H. Ueda, and B. Bryant, Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 027205 (2019), "Negative Thermal Expansion in the Plateau State of a Magnetically Frustrated Spinel"
- S. Okumura, H. Ishizuka, Y. Kato, J. Ohe, and Y. Motome, Appl. Phys. Lett. 115, 012401 (2019), "Spin-current diode with a monoaxial chiral magnet"
- S.-H. Jang, R. Sano, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 99, 241106(R) (2019), "Antiferromagnetic Kitaev interaction in f-electron based honeycomb magnets"
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Motome, T. Miyake, S. Ishibashi, and P. Werner, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 31, 323001 (2019), "First-principles studies of spin-orbital physics in pyrochlore oxides" [TOPICAL REVIEW]
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 88, 063702 (2019), "Magnetic Vortex Induced by Nonmagnetic Impurity in Ferromagnets: Magnetic Multipole and Toroidal around the Vacancy"
- K. N. Okada, Y. Kato, and, Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 99, 134442 (2019), "Magnetoelectric effect in band insulator-ferromagnet heterostructures"
- S. Hayami, Y. Yanagi, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 147602 (2019), "Electric Toroidal Quadrupoles in Spin-Orbit-Coupled Metal Cd2Re2O7" [selected as Cover image]
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 99, 094420 (2019), "Effect of magnetic anisotropy on Skyrmions with a high topological number in itinerant magnets"
- Y. Kato, K. Kimura, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, A. Matsuo, K. Kindo, M. Akaki, M. Hagiwara, S. Kimura, T. Kimura, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 99, 024415 (2019), "Magnetoelectric behavior from cluster multipoles in square cupolas: Study of Sr(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4 in comparison with Ba and Pb isostructurals"
- Y. Sugita and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 99, 041101(R) (2019), "Band crossings in honeycomb-layered transition metal compounds"
- K. N. Okada, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 98, 224406 (2018), "Multiple-Q magnetic orders in Rashba-Dresselhaus metals"
- K. Kimura, Y. Kato, K. Yamauchi, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, A. Matsuo, K. Kindo, M. Akaki, M. Hagiwara, S. Kimura, M. Toyoda, Y. Motome, and T. Kimura, Phys. Rev. Mat. 2, 104415 (2018), "Magnetic structural unit with convex geometry: A building block hosting an exchange-striction-driven magnetoelectric coupling" [Editors' Suggestion]
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 137202 (2018), "Neel- and Bloch-Type Magnetic Vortices in Rashba Metals" [selected as Cover image]
- J. Nasu, Y. Kato, Y. Kamiya, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 98, 060416(R) (2018), "Successive Majorana topological transitions driven by a magnetic field in the Kitaev model"
- Y. Kasahara, T. Ohnishi, Y. Mizukami, O. Tanaka, S. Ma, K. Sugii, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, T. Shibauchi, and Y. Matsuda, Nature 559, 227 (2018), "Majorana quantization and half-integer thermal quantum Hall effect in a Kitaev spin liquid"
- R. Takashima, Y. Shiomi, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 98, 020401(R) (2018), "Nonreciprocal spin Seebeck effect in antiferromagnets"
- Y. Kasahara, K. Sugii, T. Ohnishi, M. Shimozawa, M. Yamashita, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, T. Shibauchi, and Y. Matsuda, Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 217205 (2018), "Unusual Thermal Hall Effect in a Kitaev Spin Liquid Candidate α-RuCl3"
- S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 87, 033708 (2018), "Lock-in of a Chiral Soliton Lattice by Itinerant Electrons"
- R. Takashima, Y. Kato, Y. Yanase, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 97, 081107(R) (2018), "Generation and control of noncollinear magnetism by supercurrent"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 97, 024414 (2018), "Emergent odd-parity multipoles and magnetoelectric effects on a diamond structure: Implication for the 5d transition metal oxides AOsO4 (A= K, Rb, and Cs)"
- Y. Sugita, T. Miyake, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 97, 035125 (2018), "Multiple Dirac cones and topological magnetism in honeycomb-monolayer transition metal trichalcogenides" [selected in Kaleidoscope]
- R. Sano, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 97, 014408 (2018), "Kitaev-Heisenberg Hamiltonian for high-spin d7 Mott insulators"
- Y. Kato, Y. Kamiya, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 96, 174409 (2017), "Chiral spin liquids at finite temperature in a three-dimensional Kitaev model", Erratum
- J. Nasu, J. Yoshitake, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 127204 (2017), "Thermal Transport in the Kitaev Model"
- S.-H. Do, S.-Y. Park, J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, Y. S. Kwon, D. T. Adroja, D. J. Voneshen, K. Kim, T.-H. Jang, J.-H. Park, K.-Y. Choi, and S. Ji, Nature Physics 13, 1079 (2017), "Majorana fermions in the Kitaev quantum spin system α-RuCl3"
- P. A. Mishchenko, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 96, 125124 (2017), "Finite-temperature phase transition to a Kitaev spin liquid phase on a hyperoctagon lattice: A large-scale quantum Monte Carlo study", Erratum
- R. Ozawa, S. Hayami, K. Barros, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 96, 094417 (2017), "Shape of magnetic domain walls formed by coupling to mobile charges"
- J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 96, 064433 (2017), "Temperature evolution of spin dynamics in two- and three-dimensional Kitaev models: Influence of fluctuating Z2 fluxes"
- J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 96, 024438 (2017), "Majorana dynamical mean-field study of spin dynamics at finite temperatures in the honeycomb Kitaev model"
- S. Hayami, R. Ozawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 95, 224424 (2017), "Effective bilinear-biquadratic model for noncoplanar ordering in itinerant magnets", Erratum [selected in Kaleidoscope]
- S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 86, 063701 (2017), "Monte Carlo Study of Magnetoresistance in a Chiral Soliton Lattice"
- R. Ozawa, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 147205 (2017), "Zero-Field Skyrmions with a High Topological Number in Itinerant Magnets"
- J. Nasu, Y. Kato, J. Yoshitake, Y. Kamiya, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 137203 (2017), "Spin-Liquid-to-Spin-Liquid Transition in Kitaev Magnets Driven by Fractionalization"
- Y. Kato, K. Kimura, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, A. Matsuo, K. Kindo, M. Akaki, M. Hagiwara, M. Sera, T. Kimura, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 107601 (2017), "Magnetoelectric Behavior from S=1/2 Asymmetric Square Cupolas"
- J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 157203 (2016), "Fractional Spin Fluctuation as a Precursor of Quantum Spin Liquids: Majorana Dynamical Mean-Field Study for the Kitaev Model"
- R. Ozawa, S. Hayami, K. Barros, G-W. Chern, Y. Motome, C. D. Batista, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 85, 103703 (2016), "Vortex Crystals with Chiral Stripes in Itinerant Magnets"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Cond. Matter 28, 395601 (2016), "Emergent spin-valley-orbital physics by spontaneous parity breaking"
- S. Hayami, R. Ozawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 94, 024424 (2016), "Engineering chiral density waves and topological band structures by multiple-Q superpositions of collinear up-up-down-down orders"
- J. Nasu, J. Knolle, D. L. Kovrizhin, Y. Motome, and R. Moessner, Nature Physics 12, 912 (2016), "Fermionic response from fractionalization in an insulating two-dimensional magnet"
- Y. Sugita and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 85, 073709 (2016), "Topological Insulators from Electronic Superstructures"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 85, 053705 (2016), "Asymmetric Magnon Excitation by Spontaneous Toroidal Ordering"
- M. Naka, H. Seo, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 056402 (2016), "Theory of Valence Transition in BiNiO3"
- A. Uehara, H. Shinaoka, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 92, 195150 (2015), "Charge-spin-orbital fluctuations in mixed valence spinels: Comparative study of AlV2O4 and LiV2O4"
- Y. Kamiya, Y. Kato, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 92, 100403(R) (2015), "Magnetic three states of matter: A quantum Monte Carlo study of spin liquids", Erratum
- J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 92, 115122 (2015), "Thermal fractionalization of quantum spins in a Kitaev model: Temperature-linear specific heat and coherent transport of Majorana fermions"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 087203 (2015), "Thermodynamics of Chiral Spin Liquids with Abelian and Non-Abelian Anyons"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 92, 024415 (2015), "Strong coupling theory for electron-mediated interactions in double-exchange models"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 84, 064717 (2015), "Spontaneous Multipole Ordering by Local Parity Mixing"
- Y. Akagi and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 91, 155132 (2015), "Spontaneous formation of kagome network and Dirac half-semimetal on a triangular lattice"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 91, 085110 (2015), "Exotic magnetic phases in an Ising-spin Kondo lattice model on a kagome lattice"
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 91, 075104 (2015), "Topological semimetal-to-insulator phase transition between noncollinear and noncoplanar multiple-Q states on a square-to-triangular lattice"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, J. of Stat. Mech.: Theory and Experiment P01016 (2015), "Entanglement spectrum in cluster dynamical mean-field theory"
- J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 197205 (2014), "Vaporization of Kitaev Spin Liquids"
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 90, 165119 (2014), "Effect of magnetoelastic coupling on spin-glass behavior in Heisenberg pyrochlore antiferromagnets with bond disorder"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 90, 081115(R) (2014), "Spontaneous parity breaking in spin-orbital coupled systems"
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 90, 060402(R) (2014), "Multiple-Q instability by (d-2)-dimensional connections of Fermi surfaces"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 90, 024432 (2014), "Toroidal order in metals without local inversion symmetry" [Editors' Suggestion]
- Y. Otsuka, H. Seo, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 83, 083703 (2014), "Magnetic Field Effect in One-Dimensional Charge Ordering Systems"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 90, 045102 (2014), "Spin-orbit coupling in octamers in a spinel sulfide CuIr2S4: Competition between spin-singlet and quadrupolar states, and its relevance to remnant paramagnetism"
- R. Ozawa, M. Udagawa, Y. Akagi, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 83, 073706 (2014), "Reconstruction of Chiral Edge States in a Magnetic Chern Insulator"
- J. Nasu, T. Kaji, K. Matsuura, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 89, 115125 (2014), "Finite-temperature phase transition to a quantum spin liquid in a three-dimensional Kitaev model on a hyperhoneycomb lattice"
- S. Hayami, T. Misawa, Y. Yamaji, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 89, 085124 (2014), "Three-dimensional Dirac electrons on a cubic lattice with noncoplanar multiple-Q order"
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Motome, T. Miyake, and S. Ishibashi, Phys. Rev. B 88, 174422 (2013), "Spin-orbital frustration in molybdenum pyrochlores A2Mo2O7 (A= rare earth)" [selected in Kaleidoscope]
- Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 82, 123709 (2013), "Effect of Quantum Spin Fluctuation on Scalar Chiral Ordering in the Kondo Lattice Model on a Triangular Lattice"
- H. Ishizuka, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, Comp. Phys. Commun. 184, 2684 (2013), "Polynomial Expansion Monte Carlo Study of Frustrated Itinerant Electron Systems: Application to a Spin-ice type Kondo Lattice Model on a Pyrochlore Lattice"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 88, 100402(R) (2013), "Spontaneous spatial inversion symmetry breaking and spin Hall effect in a spin-ice double-exchange model"
- S. Sakai, S. Blanc, M. Civelli, Y. Gallais, M. Cazayous, M.-A. Measson, J. S. Wen, Z. J. Xu, G. D. Gu, G. Sangiovanni, Y. Motome, K. Held, A. Sacuto, A. Georges, and M. Imada, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 107001 (2013), "Raman-Scattering Measurements and Theory of the Energy-Momentum Spectrum for Underdoped Bi2Sr2CaCuO8+δ Superconductors: Evidence of an s-Wave Structure for the Pseudogap"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 88, 081105(R) (2013), "Loop Liquid in an Ising-Spin Kondo Lattice Model on a Kagome Lattice"
- T. Misawa, J. Yoshitake, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 246401 (2013), "Charge Order in a Two-Dimensional Kondo Lattice Model"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 87, 155156 (2013), "Thermally-induced Phases in an Ising Kondo Lattice Model on a Triangular Lattice: Partial Disorder and Kosterlitz-Thouless State"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 87, 081105(R) (2013), "Quantum anomalous Hall effect in kagome ice"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 237207 (2012), "Dirac half-metal in a triangular ferrimagnet"
- H. Ishizuka, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 81, 113706 (2012), "Magnetic Order and Charge Disproportionation in a Spin-ice type Kondo Lattice Model: Large Scale Monte Carlo Study"
- A. Miyata, H. Ueda, Y. Ueda, Y. Motome, N. Shannon, K. Penc, and S. Takeyama, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 81, 114701 (2012), "Magnetic Phases of ZnCr2O4 Revealed by Magneto-Optical Studies under Ultra-High Magnetic Fields of up to 600 T"
- S. Hayami, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 81, 103707 (2012), "Partial Disorder and Metal-Insulator Transition in the Periodic Anderson Model on a Triangular Lattice"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 257205 (2012), "Partial disorder in an Ising-spin Kondo lattice model on a triangular lattice"
- N. Onishi, K. Oka, M. Azuma, Y. Shimakawa, Y. Motome, T. Taniguchi, M. Hiraishi, M. Miyazaki, T. Masuda, A. Koda, K. M. Kojima, and R. Kadono, Phys. Rev. B 85, 184412 (2012), "Magnetic ground state of the frustrated honeycomb lattice antiferromagnet Bi3Mn4O12(NO3)"
- Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 096401 (2012), "Hidden Multiple-spin Interactions as an Origin of Spin Scalar Chiral Order in Frustrated Kondo Lattice Models"
- M. Udagawa, H. Ishizuka, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 066406 (2012), "Non-Kondo mechanism for resistivity minimum in spin ice conduction systems"
- S. Sakai, G. Sangiovanni, M. Civelli, Y. Motome, K. Held, and M. Imada, Phys. Rev. B 85, 035102 (2012), "Cluster-size dependence in cellular dynamical mean-field theory"
- M. Imada, Y. Yamaji, S. Sakai, and Y. Motome, Ann. Phys. 523, 629 (2011), "Theory of pseudogap and superconductivity in doped Mott insulators"
- H. Ishizuka, Y. Motome, N. Furukawa, and S. Suzuki, Phys. Rev. B 84, 064120 (2011), "Quantum Monte Carlo study of the formation of molecular polarizations and the antiferroelectric ordering in squaric acid crystals"
- Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. Online - News and Comments [August 10. 2011], "Spotlighting a Dance by Doublons and Holons in Mottness"
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 047204 (2011), "Spin-glass transition in bond-disordered Heisenberg antiferromagnets coupled with local lattice distortions on a pyrochlore lattice"
- J. Yoshitake and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80, 073711 (2011), "Trimer Formation and Metal-Insulator Transition in Orbital Degenerate Systems on a Triangular Lattice"
- S. Hayami, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80, 073704 (2011), "Partial Disorder in the Periodic Anderson Model on a Triangular Lattice"
- A. Miyata, H. Ueda, Y. Ueda, Y. Motome, N. Shannon, K. Penc, and S. Takeyama, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80, 074709 (2011), "Novel Magnetic Phases Revealed by Ultra-High Magnetic Field in the Frustrated Magnet ZnCr2O4"
- H. Uchigaito, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80, 044705 (2011), "Mean-field Study of Charge, Spin, and Orbital Orderings in Triangular-lattice Compounds ANiO2 (A=Na, Li, Ag)"
- H. Ishizuka, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 83, 125101 (2011), "Metal-insulator transition caused by the coupling to localized charge-frustrated systems under ice-rule local constraint"
- S. Okumura, H. Kawamura, T. Okubo, and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 79, 114705 (2010), "Novel spin-liquid states in the frustrated Heisenberg antiferromagnet on the honeycomb lattice" [Editors' Choice]
- H. Shinaoka and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 82, 134420 (2010), "Loop algorithm for classical Heisenberg models with spin-ice type degeneracy"
- S. Sakai, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, Phys. Rev. B 82, 134505 (2010), "Doped high-Tc cuprate superconductors elucidated in the light of zeros and poles of the electronic Green's function"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, Phys. Rev. B 82, 060407(R) (2010), "Electronic phase separation in the pyrochlore double-exchange model"
- Y. Akagi and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 79, 083711 (2010), "Spin chirality ordering and anomalous Hall effect in the ferromagnetic Kondo lattice model on a triangular lattice" [日本物理学会第25回(2020年)論文賞授賞論文]
- Y. Motome, K. Nakamikawa, Y. Yamaji, and M. Udagawa, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 036403 (2010), "Partial Kondo screening in frustrated Kondo lattice systems"
- T. Misawa and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 79, 073001 (2010), "Nonequilibrium Relaxation Study of the Anisotropic Antiferromagnetic Heisenberg Model on the Triangular Lattice"
- M. Udagawa, H. Ishizuka, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 226405 (2010), "Quantum Melting of Charge Ice and Non-Fermi-Liquid Behavior: An Exact Solution for the Extended Falicov-Kimball Model in the Ice-Rule Limit"
- N. Shannon, K. Penc, and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 81, 184409 (2010), "Nematic, vector-multipole, and plateau-liquid states in the classical O(3) pyrochlore antiferromagnet with biquadratic interactions in applied magnetic field"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 106409 (2010), "Chirality-driven mass enhancement in the kagome Hubbard model"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 106407 (2010), "Phase competition in the double-exchange model on the frustrated pyrochlore lattice"
- T. Ogitsu, F. Gygi, J. Reed, M. Udagawa, Y. Motome, E. Schwegler, and G. Galli, Phys. Rev. B 81, 020102(R) (2010), "Geometrical frustration in an elemental solid: An Ising model to explain the defect structure of beta-rhombohedral boron" [Editors' Suggestion]
- H. Seo and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 196403 (2009), "Spiral charge frustration in molecular conductor (DI-DCNQI)2Ag"
- S. Sakai, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 056404 (2009), "Evolution of electronic structure of doped Mott insulators - reconstruction of poles and zeros of Green's function"
- S. Sakai, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, preprint (arXiv:0904.2318), "Reply to Comment on "Evolution of electronic structure of doped Mott insulator - reconstruction of poles and zeros of Green's function" [arXiv:0904.0454] by P. Phillips"
- T. Ogitsu, F. Gygi, J. Reed, Y. Motome, E. Schwegler, and G. Galli, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 1903 (2009), "Imperfect Crystal and Unusual Semiconductor: Boron, a Frustrated Element"
- Y. Otsuka, H. Seo, Y. Motome, and T. Kato, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 77, 113705 (2008), "Finite-Temperature Phase Diagram of Quasi-One-Dimensional Molecular Conductors: Quantum Monte Carlo Study"
- T. Koretsune, Y. Motome and A. Furusaki, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 76, 074719 (2007), "Exact diagonalization study of Mott transition in the Hubbard model on an anisotropic triangular lattice"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 206405 (2007), "Charge ordering and coexistence of charge fluctuations in quasi-two-dimensional organic conductors theta-(BEDT-TTF)2X"
- D. Tahara, Y. Motome, M. Imada, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 76, 013708 (2007), "Antiferromagnetic Ising Model on Inverse Perovskite Lattice"
- H. Seo, Y. Motome and T. Kato, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 76, 013707 (2007), "Finite-temperature phase transitions in quasi-one-dimensional molecular conductors"
- K. Matsuda, N. Furukawa and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 75, 124716 (2006), "Spin Singlet State in Heptamers Emerging in Spinel Oxide AlV2O4"
- D. Phelan, D. Louca, K. Kamazawa, S.-H. Lee, S. N. Ancona, S. Rosenkranz, Y. Motome, M. F. Hundley, J. F. Mitchell and Y. Moritomo, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 235501 (2006), "Spin Incommensurability and Two Phase Competition in Cobaltites"
- Y. Horibe, M. Shingu, K. Kurushima, H. Ishibashi, N. Ikeda, K. Kato, Y. Motome, N. Furukawa, S. Mori and T. Katsufuji, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 086406 (2006), "Spontaneous Formation of Vanadium “Molecules” in a Geometrically Frustrated Crystal: AlV2O4", Erratum
- C. Sen, G. Alvarez, Y. Motome, N. Furukawa, I. A. Sergienko, T. Schulthess, A. Moreo and E. Dagotto, Phys. Rev. B 73, 224430 (2006), "One- and two-band models for colossal magnetoresistive manganites studied using the truncated polynomial expansion method"
- G. Alvarez, C. Sen, N. Furukawa, Y. Motome and E. Dagotto, Comp. Phys. Commun. 168, 32 (2005), "The Truncated Polynomial Expansion Monte Carlo Method for Fermion Systems Coupled to Classical Fields: A Model Independent Implementation"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, Phys. Rev. B 71, 014446 (2005), "Disorder effect on spin excitation in double-exchange systems"
- T. Hikihara and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 70, 214404 (2004), "Orbital and spin interplay in spin-gap formation in pyroxene ATiSi2O6 (A=Na, Li)", Erratum, ibid. 72, 179902 (2005)
- Y. Motome and H. Tsunetsugu, Phys. Rev. B 70, 184427 (2004), "Orbital and magnetic transitions in geometrically frustrated vanadium spinels: Monte Carlo study of an effective spin-orbital-lattice coupled model"
- H. Seo, Y. Motome and N. Nagaosa, Phys. Rev. B 70, 060403 (2004), "Reentrant behavior and gigantic response in a disordered spin-Peierls system"
- S. Onoda, Y. Motome and N. Nagaosa, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 236403 (2004), "Two-Dimensional Charge Order in Layered 2-1-4 Perovskite Oxides"
- N. Furukawa and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 73, 1482 (2004), "Order N Monte Carlo Algorithm for Fermion Systems Coupled with Fluctuating Adiabatical Fields"
- Y. Motome, N. Furukawa and N. Nagaosa, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 167204 (2003), "Competing Orders and Disorder-induced Insulator to Metal Transition in Manganites"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, Phys. Rev. B 68, 144432 (2003), "Monte Carlo Study of Doping Change and Disorder Effect on Double Exchange Ferromagnetism"
- H. Tsunetsugu and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 68, 060405 (2003), "Magnetic transition and orbital degrees of freedom in vanadium spinels"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 72, 2126 (2003), "Universality Class of Ferromagnetic Transition in Three-Dimensional Double-Exchange System -O(N) Monte Carlo Study-"
- Y. Motome, H. Seo, Z. Fang and N. Nagaosa, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 146602 (2003), "One-Dimensional Confinement and Enhanced Jahn-Teller Instability in LaVO3"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 72, 472 (2003), "Spectral Function Analysis on Spin Dynamics in Double-Exchange Systems with Randomness"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 71, 1419 (2002), "Anomaly in Spin Excitation Spectrum of Double-Exchange Systems with Randomness"
- S. Pankov, G. Kotliar and Y. Motome, Phys. Rev. B 66, 045117 (2002), "Semiclassical Analysis of Extended Dynamical Mean Field"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 70, 2802 (2001), "Non-equilibrium Relaxation Study of Ferromagnetic Transition in Double-Exchange Systems"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 70, 1487 (2001), "Critical Phenomena of Ferromagnetic Transition in Double-Exchange Systems"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 69, 3785 (2000), "Critical Temperature of Ferromagnetic Transition in Three-Dimensional Double-Exchange Models", Erratum, ibid. 70, 3186 (2001)
- Y. Motome and G. Kotliar, Phys. Rev. B 62, 12800 (2000), "Effects of Boson Dispersion in Fermion-Boson Coupled Systems"
- H. Nakano, Y. Motome and M. Imada, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 69, 1282 (2000), "Incoherent Charge Dynamics in Perovskite Manganese Oxides"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 68, 3853 (1999), "A Monte Carlo Method for Fermion Systems Coupled with Classical Degrees of Freedom"
- H. Nakano, Y. Motome and M. Imada, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 68, 2178 (1999), "Effects of Orbital Degeneracy and Electron Correlation on Charge Dynamics in Perovskite Manganese Oxides"
- Y. Motome and M. Imada, Phys. Rev. B 60, 7921 (1999), "Ordering and Fluctuation of Orbital and Lattice Distortion in Perovskite Manganese Oxides"
- Y. Motome and M. Imada, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 68, 16 (1999), "Effects of Electron Correlation, Orbital Degeneracy and Jahn-Teller Coupling in Perovskite Manganites"
- Y. Motome and M. Imada, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 67, 3199 (1998), "Numerical Study for the Ground State of Multi-Orbital Hubbard Models"
- Y. Motome and M. Imada, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 66, 1872 (1997), "A Quantum Monte Carlo Method and Its Applications for Multi-Orbital Hubbard Models"
- Y. Motome,N. Katoh, N. Furukawa and M. Imada, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 65, 1949 (1996), "Impurity Effect on Spin Ladder System"
- Y. Motome and M. Imada, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 65, 2135 (1996), "Superfluid-Insulator Transition of Interacting Multi-Component Bosons -Gutzwiller Variational and Quantum Monte Carlo Study-"
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Motome, New Phys.: Sae Mulli 73 1155 (2023), "Video Recognition by Physical Reservoir Computing in Magnetic Materials"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2164 012069 (2022), "Phase shift, ellipticity, angle, and topological number in skyrmion lattices"
- S. Okumura, T. Morimoto, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2164 012068 (2022), "Electrical conductivity in helical and conical magnetic states"
- S. Hayami, Y. Yanagi, M. Naka, H. Seo, Y. Motome, and H. Kusunose, JPS Conf. Proc. 30, 011149 (2020), "Multipole Description of Emergent Spin-Orbit Interaction in Organic Antiferromagnet κ-(BEDT-TTF)2Cu[N(CN)2]Cl"
- S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, JPS Conf. Proc. 30, 011010 (2020), "Tracing Monopoles and Anti-monopoles in a Magnetic Hedgehog Lattice"
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, IEEE Trans. Mag. 55, 0018-9464 (2018), "Multiple-Q Magnetic States in Spin-Orbit Coupled Metals"
- Y. Kato, Y. Kamiya, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, Physica B: Cond. Matter 536, 405 (2018), "Global constraints on Z2 fluxes in two different anisotropic limits of a hypernonagon Kitaev model"
- S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, Physica B: Cond. Matter 536, 223 (2018), "Chiral helimagnetic state in a Kondo lattice model with the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction"
- Y. Sugita, T. Miyake, and Y. Motome, Physica B: Cond. Matter 536, 48 (2018), "Electronic band structure of 4d and 5d transition metal trichalcogenides"
- R. Ozawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 807, 102005 (2017), "Simulated floating zone method"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 683, 012037 (2016), "Spin correlation and Majorana spectrum in chiral spin liquids in a decorated-honeycomb Kitaev model"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, Physics Procedia 75, 755 (2015), "Phase Diagram of the Kitaev-type Model on a Decorated Honeycomb Lattice in the Isolated Dimer Limit"
- A. Uehara, H. Shinaoka, and Y. Motome, Physics Procedia 75, 495 (2015), "Analysis of Charge-spin-orbital Fluctuations by Ab Initio Calculation and Random Phase Approximation: Application to Non-coplanar Antiferromagnet Cd2Os2O7"
- Y. Sugita, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, Physics Procedia 75, 419 (2015), "Antisymmetric Spin-Orbit Coupling in a d-p Model on a Zigzag Chain"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 592, 012131 (2015), "Quantum spin Hall effect in a two-orbital model on a honeycomb lattice"
- R. Ozawa, M. Udagawa, Y. Akagi, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 592, 012130 (2015), "Surface and interface effects on a magnetic Chern insulator"
- J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 592, 012115 (2015), "Low-energy Majorana states in spin-liquid transitions in a three-dimensional Kitaev model"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 592, 012101 (2015), "Toroidal order in a partially disordered state on a layered triangular lattice: implication to UNi4B"
- S. Hayami, T. Misawa, and Y. Motome, JPS Conf. Proc. 3, 016016 (2014), "Charge Order with a Noncoplanar Triple-Q Magnetic Order on a Cubic Lattice"
- Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, JPS Conf. Proc. 3, 014017 (2014), "Linear Spin Wave Analysis for General Magnetic Orders in the Double-Exchange Model"
- H. Ishizuka, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, JPS Conf. Proc. 3, 014013 (2014), "Monte Carlo Study of an Effective Ising Model for the Spin-ice type Kondo Lattice Model"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, JPS Conf. Proc. 3, 014010 (2014), "On the Stability of Quantum Hall Kagome-ice Insulator"
- M. Udagawa, H. Ishizuka, and Y. Motome, JPS Conf. Proc. 3, 014009 (2014), "Invariant Energy Levels and Flat Band Engineering in a Kondo Lattice Model on Geometrically Frustrated Lattices"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 63, 579 (2013), "Thermally-induced magnetic phases in an Ising spin Kondo lattice model on a kagome lattice at 1/3-filling"
- Y. Akagi and Y. Motome, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 63, 405 (2013), "Ground-state phase diagram of the Kondo lattice model on triangular-to-kagome lattices"
- M. Imada, S. Sakai, Y. Yamaji, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 449, 012005 (2013), "Theory of Pseudogap in Underdoped Cuprates"
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 400, 032087 (2012), "Critical property of spin-glass transition in a bond-disordered classical antiferromagnetic Heisenberg model with a biquadratic interaction"
- H. Ishizuka, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 400, 032027 (2012), "Application of polynomial-expansion Monte Carlo method to a spin-ice Kondo lattice model"
- S. Hayami, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 400, 032018 (2012), "Carrier doping to a partially disordered state in the periodic Anderson model on a triangular lattice"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 320, 012060 (2011), "Orbital degeneracy and Mott transition in Mo pyrochlore oxides"
- Y. Akagi and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 320, 012059 (2011), "Noncoplanar spin canting in lightly-doped ferromagnetic Kondo lattice model on a triangular lattice"
- H. Ishizuka, Y. Motome, N. Furukawa, and S. Suzuki, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 320, 012054 (2011), "Quantum Monte Carlo study of the transverse-field Ising model on a frustrated checkerboard lattice"
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 320, 012009 (2011), "Loop algorithm for classical antiferromagnetic Heisenberg models with biquadratic interactions"
- Y. Motome, K. Nakamikawa, Y. Yamaji, and M. Udagawa, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80, Suppl. A, SA133 (2011), "Variational Monte Carlo Study of the Kondo Necklace Model with Geometrical Frustration"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 200, 012131 (2010), "Ferromagnetic transition in the double-exchange model on the pyrochlore lattice"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 200, 012214 (2010), "Chirality-spin separation in the Hubbard model on the kagome lattice"
- Y. Otsuka, H. Seo, and Y. Motome, Physica B: Cond. Mat. 405, S317 (2010), "Charge ordering due to pi-d coupling in one-dimensional system"
- S. Sakai, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, Physica B: Cond. Mat. 404, 3183 (2009), "Roles of zeros of the Green function in Fermi arc and non-Fermi liquid in the two-dimensional Hubbard model"
- Y. Motome, Y. Yamaji, and M. Udagawa, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 145, 012068 (2009), "Instability to partial Kondo-singlet state in the Kondo necklace model on frustrated lattices"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 145, 012013 (2009), "Cluster dynamical mean-field study of the Hubbard model on a 3D frustrated hyperkagome lattice"
- Y. Otsuka, H. Seo, Y. Motome, and T. Kato, Physica B: Cond. Matter 404, 479 (2009), "Phase competitions and coexistences in quasi-one-dimensional molecular conductors: Exact diagonalization study"
- K. Penc, N. Shannon, Y. Motome, and H. Shiba, J. Phys.: Cond. Matter 19, 145267 (2007), "Symmetry considerations on the magnetization process of the Heisenberg model on the pyrochlore lattice"
- N. Shannon, H. Ueda, Y. Motome, K. Penc, H. Shiba, and H. Takagi, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 51, 31 (2006), "Half-magnetization plateaux in Cr spinels"
- Y. Motome, K. Penc, and N. Shannon, J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 300, 57 (2006), "Monte Carlo study of half-magnetization plateau and magnetic phase diagram in pyrochlore antiferromagnetic Heisenberg model"
- Y. Motome and H. Tsunetsugu, Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 160, 203 (2005), "Theory of successive transitions in vanadium spinels and order of orbitals and spins"
- Y. Motome, H. Tsunetsugu, T. Hikihara, N. Shannon, and K. Penc, Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 159, 314 (2005), "Interplay among Spin, Orbital and Lattice Degrees of Freedom in t2g Electron Systems with Edge-Sharing Network of Octahedra"
- T. Hikihara and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 74Suppl., 212 (2005), "Phase transitions in spin-orbital coupled model for pyroxene titanium oxides"
- Y. Motome and H. Tsunetsugu, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 74Suppl., 208 (2005), "Spin Frustration and Orbital Order in Vanadium Spinels"
- N. Furukawa and Y. Motome, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 74Suppl., 203 (2005), "Colossal magnetoresistance and quenched disorder in manganese oxides"
- Y. Motome and H. Tsunetsugu, Physica B 359-361, 1222 (2005), "Orbital ordering and one-dimensional magnetic correlation in vanadium spinel oxides AV2O4 (A = Zn, Mg, or Cd)"
- N. Furukawa, Y. Motome, and N. Nagaosa, Physica B 359-361, 1228 (2005), "Entropy-Driven Reentrant Behavior in CMR Manganites"
- Y. Motome, N. Furukawa, and N. Nagaosa, Lecture Notes in Physics 678, 71 (ed. by M. Donath and W. Nolting, Springer-Verlag, 2005), "An Origin of CMR: Competing Phases and Disorder-Induced Insulator-to-Metal Transition in Manganites"
- Y. Motome, N. Furukawa, and N. Nagaosa, J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 272-276, 1805 (2004), "Randomness Effect on Multicritical Phenomena in Double-Exchange Systems"
- N. Furukawa and Y. Motome, Physica B 329-333, 759 (2003), "Spin-Wave Hamiltonian in Double-Exchange Systems"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 63, 1357 (2002), "Impurity Effect on Ferromagnetic Transition in Double-Exchange Systems"
- N. Furukawa and Y. Motome, Appl. Phys. A 74Suppl., 1728 (2002), "Critical exponents for the ferromagnetism in colossal magnetoresistance manganites"
- N. Furukawa, Y. Motome, and H. Nakata, Comp. Phys. Commun. 142, 410 (2001), "Monte Carlo algorithm for the double exchange model optimized for parallel computations"
- Y. Motome and G. Kotliar, Proceedings to International Symposium on Physics in Local Lattice Distortions (AIST Tsukuba, Japan, 2000. July.23-26), "Fluctuation Effects by Boson Dispersion in Fermion-Boson Coupled Systems"
- H. Nakano, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, Physica B 284-288, 1406 (2000), "Charge dynamics of perovskite manganese oxides - effects of orbital degeneracy, electron correlation and Jahn-Teller distortion"
- Y. Motome, H. Nakano, and M. Imada, Material Science and Engineering B 63, 58 (1999), "Metal-Insulator Transition in Mn Perovskite Compounds"
- M. Imada, F. F. Assaad, H. Tsunetsugu, and Y. Motome, in Physics and Chemistry of Transition Metal Oxides, Proceedings of 20th Taniguchi Symposium, ed. by H. Fukuyama and N. Nagaosa (Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1999), "Metal-Insulator and Superconductor-Insulator Transitions in Correlated Electron Systems"
- Y. Motome and M. Imada, Proceedings to APCTP/ICTP Joint International Conference on Highlights in Condensed Matter Physics (Seoul, Korea, 1998. June.12-16), "Effects of Electron Correlation and Jahn-Teller Distortion in Doped Perovskite Manganites"
- Y. Motome and M. Imada, Proceedings to the 9th International Conference Recent Progress in Many-Body Theories, ed. by D. Neilson and R. F. Bishop (World Scientific, 1998), "Ground State Properties of Doubly Degenerate Hubbard Models: Quantum Monte Carlo Study"
- N. Katoh, Y. Motome, N. Furukawa, and M. Imada, J. Low. Temp. Phys. 105, 62 (1996), "Spin Gap and Antiferromagnetic Fluctuation in Spin Ladder System Doped with Nonmagnetic Impurities"
Talks (click to show/hide)
FY2025
- Y. Motome, "Competing phases and transport phenomena in the Kitaev model and its extensions", Advanced School and Conference on Quantum Matter, Trieste, Italy (Dec. 2025)
- Y. Motome, "Probing Majorana-mediated heat and spin transport in Kitaev spin liquids", CJoint ICTP-WE Heraeus School and Workshop on Advances in Quantum Matter: Pushing the Boundaries, Trieste, Italy (Aug. 2025)
- K. Shimizu, "Zero-to-Perfect Toron Hall Effect in Chiral Magnets", Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems 2025 (SCES2025), Montreal, Canada (Jul. 2025)
FY2024
- Y. Motome, "Altermagnet: Revealing new functionalities in antiferromagnets", CREST-EPiQS International Workshop 2024, Kyoto, Japan (Dec. 2024)
- K. Inui, "Inverse Hamiltonian design of highly-entangled quantum many-body systems", ISSP Theory mini-Workshop: Correlated Quantum Materials + beyond (Symposium), ISSP, Univ. of Tokyo, Japan (Nov. 2024)
- K. Shimizu, "Current-induced dynamics of magnetic hedgehog lattice", ISSP Theory mini-Workshop: Correlated Quantum Materials + beyond, ISSP, Univ. of Tokyo, Japan (Nov. 2024)
- K. Fukui, "Kitaev spin liquid coupled to environment", ISSP Theory mini-Workshop: Correlated Quantum Materials + beyond, ISSP, Univ. of Tokyo, Japan (Nov. 2024)
- S. Okumura, "Emergent magnetic monopole-antimonopole lattices in centrosymmetric metals", International Conference on Complexity and Topology in Quantum Matter (CT.QMAT24), Dresden, Germany (Sep. 2024)
- Y. Motome, "Kitaev spin liquid: from materials design to experimental observation", The 5th international workshop on quantum matter – quantum magnetism, Kunming, China (Aug. 2024)
- K. Fukui, "Topological Majorana flat bands in the Kitaev model on a Bishamon-kikko lattice", International Conference on New Frontiers in Advanced Magnetism 2024, Sapporo, Japan (Aug. 2024)
- K. Kobayashi, "Signatures of quantum phase transitions in local quench dynamics by quantum reservoir probling", International Conference on New Frontiers in Advanced Magnetism 2024, Sapporo, Japan (Aug. 2024)
- Y. Motome, "Topological spin moire: stability, dynamics, and controllability", SPICE workshop, Spin textures: Magnetism meets Plasmonics, Ingelheim, Germany (Jul. 2024)
- Y. Motome, "Topological spin superstructures stabilized by itinerant frustration", International Conference on Magnetism (ICM2024), Bologna, Italy (Jun.-Jul. 2024)
- K. Fukui, "Topological Majorana flat bands in the Kitaev model on a Bishamon-kikko lattice", International Conference on Magnetism (ICM2024), Bologna, Italy (Jun.-Jul. 2024)
- S. Okumura, "Emergent magnetic monopole lattices in centrosymmetric metals", International Conference on Magnetism (ICM2024), Bologna, Italy (Jun.-Jul. 2024)
- K. Kobayashi, "Quantum reservoir probing for the detection of quantum phase transitions", International Conference on Magnetism (ICM2024), Bologna, Italy (Jun.-Jul. 2024)
- K. Shimizu, "Current-induced dynamics of magnetic hedgehog lattices", Sol-SKYMAG 2024, San Sebastian, Spain (Jun. 2024)
- Y. Motome, "Computational design of Kitaev magnet heterostructures", Progress in 2D Kitaev Materials, St. Louis, USA (May. 2024)
FY2023
- Y. Kato, "Spin Seebeck effect in the Kitaev spin liquid", CEMS Symposium on Emergent Quantum Materials 2024, Tokyo, Japan (Feb. 2024)
- S. Okumura, "Versatile magnetic hedgehog lattice phases induced by anisotropic interactions in centrosymmetric systems", International Symposium on Quantum Electronics, Tokyo, Japan (Feb. 2024)
- K. Kobayashi, "Quantum reservoir probing as a witness for information scrambling", 1st International Workshop on Quantum Information Engineering (QIE2023), Okinawa, Japan (Oct. 2023)
- S. Okumura, "Instability of skyrmion strings induced by longitudinal spinpolarized currents", Trends in MAGnetism 2023, Rome, Italy (Sep. 2023)
- K. Fukui, "Effect of a magnetic field on the Kitaev model coupled to environment", Physics of Open Systems and Beyond (POS&BYD), Sapporo, Japan (Aug. 2023)
- K. Kobayashi, "Thermal robustness and spatiotemporal parallelization of physical reservoir computing in magnetic materials", 28th International Conference on Statistical Physics (Statphys28), Tokyo, Japan (Aug. 2023)
- Y. Motome, "Computational design of Kitaev materials", International Conference on Quantum Liquid Crystals 2023 (QLC2023), Sapporo, Japan (Aug. 2023)
- S. Okumura, "Magnetic Hedgehog Lattices in Itinerant Magnets", International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES2023), Incheon, Korea (Jul. 2023)
- K. Nakazawa, "Layer Number Dependence of Topological Properties in Thin Films of a Ferromagnetic Weyl Semimetal Co-Based Shandite", International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES2023), Incheon, Korea (Jul. 2023)
- Y. Motome, "Topological Transitions between Topological Spin Crystals Stabilized by Itinerant Frustration", International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES2023), Incheon, Korea (Jul. 2023)
- R. Pohle, "Spin Nematics Meet Spin Liquids: Exotic Phases in the Spin-1 Bilinear-Biquadratic Model with Kitaev Interactions", International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES2023), Incheon, Korea (Jul. 2023)
- Y. Motome, "Nonequilibrium Spin Dynamics in Kitaev Spin Liquids", Quantum Magnetism and Topology (QMT2023), Pohang, Korea (Jun. 2023)
- Y. Motome, "Kitaev magnets as a Majorana platform", 8th International Conference on Superconductivity and Magnetism (ICSM2023), Fethiye, Turkey (May 2023)
FY2022
- Y. Motome, "Materials perspective on Kitaev spin liquids", International workshop on Novel Quantum States in Condensed Matter 2022 (NQS2022), Kyoto (hybrid) (Nov.-Dec. 2022)
- Y. Motome, "Topological spin crystals by itinerant frustration", Frustrated Metals and Insulators, Bengaluru, India (hybrid) (Sep. 2022)
- R. Pohle, "Spin liquid and nematic states in the spin-1 honeycomb Kitaev model with bilinear-biquadratic interactions", 29th International Conference on Low Temperature Physics (LT29), Sapporo (Hybrid) (Aug. 2022)
- Y. Motome, "Kitaev spin liquid materials as a Majorana platform", International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems 2022 (SCES2022), Amsterdam (Jul. 2022)
- K. Shimizu, "Phase degree of freedom and topological properties in multiple-Q spin textures", International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems 2022 (SCES2022), Amsterdam (Jul. 2022)
- K. Shimizu, "Spin moire engineering of topology and emergent electromagnetic fields in multiple-Q spin textures", 11th International Conference on Highly Frustrated Magnetism 2022 (HFM2022), Paris (Hybrid) (Jun. 2022)
FY2021
- K. Shimizu, "Phase degree of freedom and topological properties of multiple-Q spin textures", International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES2020/21), Online (Sep. 2021)
- S. Okumura, "Quadratic optical responses in a chiral magnetic metal", International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES2020/21), Online (Sep. 2021)
- Y. Motome, "Topological spin crystals stabilized by itinerant frustration", Invited talk in 84. Jahrestagung der DPG und DPG-Tagung der (84th Annual Meeting of the German Physical Society meeting), Online (Sep. 2021)
- Y. Motome, "Topological spin moire and emergent electromagnetism", International Conference on Quantum Liquid Crystals 2021 (QLC2021), Online (May 2021)
FY2020
- Y. Motome, "Majorana fermions in the Kitaev model: past, present, and future", 10th Workshop on Semiconductor/Superconductor Quantum Coherence Effect and Quantum Information, Online (Dec. 2020)
- S.-H Jang, "Computational design of f-electron based Kitaev spin liquids", KITP workshop: Correlated Systems with Multicomponent Local Hilbert Spaces, Santa Barbara, USA (online) (Oct. 2020)
- S. Okumura, "Topological Magnetic Textures with Monopoles in Chiral Metals", Quantum Complex Matter 2020, Rome, Italy (online) (Jun. 2020)
- K. Shimizu, "Phase transitions between helices, vortices, and hedgehogs in chiral magnets by controlling spatial anisotropy", Quantum Complex Matter 2020, Rome, Italy (online) (Jun. 2020)
FY2019
- Y. Kato, "Three-dimensional chiral spin liquids in hypernonagon Kitaev model", The 3rd Asia-Pacific workshop on Quantum Magnetism, Shanghai, China (Nov. 2019)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana signatures in Kitaev magnets under magnetic fields", The 3rd Asia-Pacific workshop on Quantum Magnetism, Shanghai, China (Nov. 2019)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana Excitations in Kitaev Magnets under a Magnetic Field", 14th Asia-Pacific Physics Conference (APPC 2019), Kuching, Malaysia (Nov. 2019)
- Y. Motome, "Fractional spin dynamics in Kitaev magnets", KITP Conference: Topological Quantum Matter: From Fantasy to Reality, Santa Barbara, USA (Oct. 2019)
- S. Okumura, "Numerical study on magnetic hedgehog lattices in noncentrosymmetric metals", JSPS Core-to-Core Program International meeting “Core-to-Core Final Meeting in Jaca (2019)“, Jaca, Spain (Sep. 2019)
- Y. Motome, "Fractional Majorana excitations in Kitaev spin liquids", The 5th Conference on Condensed Matter Physics, Liyang, China (Jun. 2019)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana signatures in proximate Kitaev spin liquids", International Conference on Frontiers of Correlated Electron Sciences, Tokyo, Japan (May. 2019)
- Y. Motome, "Hunting Majorana fermions in Kitaev magnets", CEMS Symposium on Emergent Quantum Materials, Tokyo, Japan (May. 2019)
FY2018
- Y. Motome, "Majorana Fermions in Topological Magnets", MANA International Symposium 2019: Toward Perceptive Nanomaterials, Devices and Systems, Tsukuba, Japan (Mar. 2019)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana fermions in honeycomb Kitaev magnets", The 8th Indo-Japan Seminar: Designing Emergent Materials, Tokyo, Japan (Jan. 2019)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana and flux excitations in Kitaev spin liquids", Workshop on Spin-orbit Coupled Topological States, Pohang, Korea (Oct. 2018)
- R. Takashima, "Nonreciprocal spin Seebeck effect in antiferromagnets", International Seminar: Frustration, Orbital Fluctuations, and Topology in Kondo Lattices and their relatives (fotok18), Dresden, Germany (Jul. 2018)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana fermions in Kitaev magnets: beyond Ir and Ru compounds", International Workshop: Frustration, Orbital Fluctuations, and Topology in Kondo Lattices and their relatives (fotok18), Dresden, Germany (Jul. 2018)
- S. Okumura, "Numerical study of spin-charge coupled phenomena in a chiral soliton lattice", International Seminar: Frustration, Orbital Fluctuations, and Topology in Kondo Lattices and their relatives (fotok18), Dresden, Germany (Jul. 2018)
- Y. Motome, "Vortices and Skyrmions In Itinerant Magnets", International Conference on Magnetism 2018 (ICM2018), Moscone Center, San Fransisco (Jul. 2018)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana signatures in Kitaev quantum spin liquids in a magnetic field", International Conference on Highly Frusturated Magnetism 2018 (HFM2018), Univ. of California, Davis (Jul. 2018)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana fermions in Kitaev spin liquids", Trends in Quantum Magnetism, 673. Wilhelm und Else Heraeus-Seminar, Physikzentrum Bad Honnef, Germany (Jun. 2018)
FY2017
- Y. Motome, "Thermal Fractionalization in Kitaev Quantum Spin Liquids", Invited talk in 2018 APS March meeting, Los Angeles, California, USA (Mar. 2018)
- Y. Motome, "Fractional spin excitations in quantum spin liquids", Max Planck-UBC-UTokyo School: Elementary Excitations in Quantum Materials, Tokyo, Japan (Feb. 2018)
- Y. Sugita, "Multiple Dirac cones and spontaneous quantum anomalous Hall state in transition metal trichalcogenides", Yukawa International workshop: Novel Quantum States in Condensed Matter 2017 (NQS2017), Kyoto, Japan (Oct. 2017)
- Y. Motome, "Fractional spin in quantum spin liquids", International workshop Frontiers in Strongly Correlated Electron System, Sapporo, Japan (Oct. 2017)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana fermions in Kitaev magnets", J-Physics 2017: International Workshop on Multipole Physics and Related Phenomena, Hachimantai, Japan (Sep. 2017)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana fermions in Kitaev spin liquids", 1st Asia Pacific Workshop on Quantum Magnetism, Seoul, Korea (Aug. 2017)
- Y. Motome, "Correlated Dirac electrons and topological magnetism in transition metal trichalcogenides", CEMS Topical Meeting on Emergent 2D Materials 2017, RIKEN, Japan (Jul. 2017)
- S. Okumura, "Quantum Monte Carlo study of magnetoresistance in a chiral soliton lattice", International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES 2017), Prague, Czech Republic (Jul. 2017)
FY2016
- Y. Motome, "Evincing Majorana fermions in Kitaev magnets", APCTP-Quantum Materials Symposium 2017 in conjunction with 17th Korea-Taiwan-Japan Workshop on SCES & APW, Yongpyong, Korea (Mar. 2017)
- Y. Motome, "Diagnostic of fractionalized Kitaev spin liquids", 14th Bilateral Japanese-German Symposium, Sapporo, Japan (Sep. 2016)
- Y. Motome, "Fractional Spin Fluctuation as a Precursor of Quantum Spin Liquids", 8th International Conference on Highly Frustrated Magnetism (HFM 2016), Taipei, Taiwan (Sep. 2016)
- Y. Motome, "Exotic orders on the Kondo lattices: from classical to quantum", Quantum Criticality and Topology in Itinerant Electron Systems, Albuquerque, USA (Aug. 2016)
- Y. Motome, "Majoranization in Kitaev spin liquids", Plenary talk in The 2nd Conference on Condensed Matter Physics (CCMP2016), Nanjing, China (Jul. 2016)
FY2015
- Y. Motome, "Thermodynamics of Fractional Quantum Spin Liquids", Invited talk in Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft e.V. (DPG: German Physical Society meeting), Regensburg, Germany (Mar. 2016)
- Y. Motome, "Hunting Majorana fermions in quantum spin liquids: Quantum Monte Carlo studies of Kitaev-type models", KITP Conference: Novel States in Spin-Orbit Coupled Quantum Matter: from Models to Materials, Santa Barbara, USA (Jul. 2015)
- Y. Motome, "Emergent spin texture and band topology in frustrated itinerant magnets", Overview talk in Advanced Working Group on Itinerant Frustration 2015 (AWGIF 2015), Trinity College, Univ. of Cambridge, UK (Jul. 2015)
- Y. Motome, "Thermodynamics of Quantum Spin Liquids", Workshop on "Topological Magnets", RIKEN, Japan (May. 2015)
- Y. Motome, "Quantum Monte Carlo study of Kitaev spin liquids", SPICE-Workshop on Computational Quantum Magnetism, Mainz, Germany (May. 2015)
FY2014
- Y. Motome, "Vaporization of Kitaev spin liquids", Frontiers in Condensed Matter Physics, Seoul, Korea (Dec. 2014)
- M. Udagawa, "Novel routes for monopole freezing in spin ice", YITP Long-term Workshop: Novel Quantum States in Condensed Matter 2014, Kyoto, Japan (Nov. 2014)
- Y. Motome, "Vaporization in quantum spin liquids", YITP Long-term Workshop: Novel Quantum States in Condensed Matter 2014, Kyoto, Japan (Nov. 2014)
- S. Hayami, "Toroidal order in metals without local inversion symmetry", Swiss-Japan Workshop 2014: Trends in Theory of Correlated Materials, Aoyama-Gakuin Univ., Japan (Oct. 2014)
- Y. Motome, "On the vaporization of Kitaev quantum spin liquids", 13th Bilateral German-Japanese Symposium: Interplay of Spin- and Orbital Degrees of Freedom in Strongly Correlated Electron Systems, Ringberg Castle, Germany (Jul. 2014)
- Y. Motome, "How does the Kitaev spin liquid evaporate?", The International Conference on Highly Frustrated Magnetism (HFM 2014), Cambridge, England (Jul. 2014)
- M. Udagawa, "Domain wall creation by electric current in All-in/All-out magnets", ISSP International Workshop on New Horizon of Strongly Correlated Physics, Tokyo, Japan (Jun. 2014)
- Y. Motome, "Vaporization of a quantum spin liquid", ISSP International Workshop on New Horizon of Strongly Correlated Physics, Tokyo, Japan (Jun. 2014)
- M. Udagawa, "Transport theory of pyrochlore conductors", OIST International Workshop on Novel Quantum Materials and Phases, Okinawa, Japan (May. 2014)
FY2013
- M. Udagawa, "Itinerant Spin Ice", Invited talk in 2014 APS March Meeting, Denver, Colorado, USA (Mar. 2014)
- Y. Motome, "Numerical study of frustration and topology in spin-charge coupled systems", Recent Developments in Computer Simulational Studies in Condensed Matter Physics, Athens, Georgia, USA (Feb. 2014)
- Y. Motome, "How does quantum spin liquid vaporize?", FIRST International Symposium on Topological Quantum Technology, Tokyo, Japan (Jan. 2014)
- Y. Motome, "Breathing-type bond order and spin Hall effect in itinerant spin ice", FIRST-QS2C Workshop on Emergent Phenomena of Correlated Materials, Tokyo, Japan (Nov. 2013)
- Y. Motome, "Large scale simulation toward new electronics and spintronics", Frontiers in Nano-Scale Physics, UTokyo Forum, Santiago, Chili (Nov. 2013)
- M. Udagawa, "Topological defects in pyrochlore conductors", International Workshop for Young Researchers on Topological Quantum Phenomena in Condensed Matter with Broken Symmetries 2013, Okinawa, Japan (Oct. 2013)
- M. Udagawa, "Transport theory of spin-ice conduction systems", The International Conference on Strongly Correlated Electron Systems (SCES 2013), Tokyo, Japan (Aug. 2013)
- Y. Motome, "Quantum anomalous Hall insulator in kagome ice", Disorder, Dynamics, Frustration and Topology in Quantum Condensed Matter, Aspen, USA (Jun. 2013)
- H. Ishizuka, "Monte Carlo Study of Spin-Ice type Kondo Lattice Model", Emergent Quantum Phases in Condensed Matter, Tokyo, Japan (Jun. 2013)
FY2012
- Y. Motome, "Spin-charge interplay on frustrated lattices", Invited talk in 2013 APS March Meeting, Baltimore, Maryland, USA (Mar. 2013)
- Y. Motome, "Frustration in elemental boron", Japan-France Joint Seminar 2012: Physics and Control of Clustering Solids, Awaji Yumebutai, Japan (Nov. 2012)
- M. Udagawa, "Transport theory of conduction electrons coupled with spin ice", Swiss-Japan Workshop 2012: Current Topics in Theory of Correlated Materials, Wako, Japan (Sep. 2012)
- H. Ishizuka, "Monte Carlo study of frustrated Ising-spin Kondo lattice models: Partial disorder and Kosterlitz-Thouless transition", International Workshop on Recent Developments of Studies on Phase Transitions 2012, Tokyo, Japan (Jun. 2012)
- Y. Motome, "Frustration, competing interactions & partial disorder in Kondo lattice systems", The International Conference on Highly Frustrated Magnetism (HFM 2012), McMaster Univ., Canada (Jun. 2012)
- Y. Motome, "Complex spin-charge orders in Kondo lattice systems", International Workshop on Itinerant Spin-Orbital Systems: From Magnetic Frustration to Novel Superconductivity, Dresden, Germany (May 2012)
- M. Udagawa, "Non-Kondo resistivity minimum in spin ice conduction systems", International Workshop on Itinerant Spin-Orbital Systems: From Magnetic Frustration to Novel Superconductivity, Dresden, Germany (May 2012)
FY2011
- Y. Motome, "Frustration in Kondo lattice systems", UK-Japan Meeting 2012 in Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan (Jan. 2012)
- Y. Motome, "Spin-glass transition in pyrochlore Heisenberg Antiferromagnets: Effect of magnetoelastic coupling", Frustrated Magnets: FROM SPIN ICE TO KAGOME PLANES, Natal, Brazil (Dec. 2011)
- Y. Motome, "Emergent order and fluctuation in frustrated spin-charge coupled systems - spin chirality, partial disorder, and spin ice", Novel Quantum States in Condensed Matter 2011 (NQS2011), Kyoto, Japan (Nov. 2011)
- Y. Motome, "Theoretical study of spin-charge coupled systems on geometrically frustrated lattices", Tokyo-Cologne Workshop on Strongly Correlated Transition-Metal Compounds, Cologne, Germany (Sep. 2011)
- Y. Motome, "Emergent order in spin-charge coupled systems on frustrated lattices", CIFAR/MEXT Japanese Network Meeting, Vancouver, Canada (May 2011)
- Y. Motome, "Emergent Order in Spin-Charge Coupled Systems on Frustrated Lattices", Novel Phenomena in Frustrated Systems, Santa Fe, USA (May 2011)
FY2010
- Y. Motome, "Emergent order in frustrated Kondo lattice systems", International Conference on Frustration in Condensed Matter (ICFCM), Sendai, Japan (Jan. 2011)
- M. Udagawa, "Geometrical frustration in itinerant electron systems", Japan-Swiss Joint Workshop, New Trends in Theory of Correlated Materials, Chiba, Japan (Sep. 2010)
- M. Udagawa, "Quantum criticality in itinerant ice-rule systems", International Conference on Highly Frustrated Magnetism 2010, Baltimore, USA (Aug. 2010)
- Y. Motome, "Spin-charge-orbital coupled phenomena in Mo pyrochlore oxides: Monte Carlo study of the pyrochlore double-exchange model", International Conference on Highly Frustrated Magnetism 2010, Baltimore, USA (Aug. 2010)
- M. Udagawa, "Quantum criticality in itinerant ice-rule systems", International Conference on Statistical Physics XXIV, Cairns, Australia (Jul. 2010)
FY2009
- Y. Motome, "Spin-charge interplay in frustrated itinerant systems", International Symposium on Physics of New Quantum Phases in Superclean Materials, Yokohama, Japan (Mar. 2010)
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, "Phase competition and large residual entropy in the pyrochlore double-exchange system", International Conference on Magnetism 2009, Karlsruhe, Germany (Jul. 2009)
- Y. Motome, "Phase competition in the pyrochlore double exchange system", Joint European Japanese Conference: Frustration in Condensed Matter, Lyon, France (May 2009)
FY2008
- Y. Motome, "Phase competitions in frustrated spin-charge coupled systems", International Workshop on Quantum Critical Phenomena and Novel Phases in Superclean Materials, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA (Jan. 2009)
- M. Udagawa, "Emergent correlations and Mott criticality - cluster dynamical mean-field study", International Workshop on Quantum Critical Phenomena and Novel Phases in Superclean Materials, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA (Jan. 2009)
FY2007
- Y. Motome, "Orbital and Magnetic Physics in Vanadium Spinels", KITP Program: Moments and Multiplets in Mott Materials, Santa Barbara, USA (Sep. 2007)
- Y. Motome, "Degeneracy and Symmetry Breaking in Spinel Oxides", NSFC-JSPS Joint Mini-Workshop on Novel Quantum Phenomena in Strongly Correlated Electronic Systems, Beijing, China (Jun. 2007)
FY2006
- Y. Motome, K. Penc and N. Shannon, "Magnetization Plateau and Magnetic Phase Diagram of Highly-Frustrated Pyrochlore Heisenberg Magnets", International Conference on Magnetism 2006, Kyoto, Japan (Aug. 2006)
- Y. Motome, "Metamagnetism and related critical phenomena in pyrochlore Heisenberg antiferromagnets", ISSP International Symposium on Computational Approaches to Quantum Critical Phenomena, ISSP, Kashiwa, Japan (Aug. 2006)
- Y. Motome, "Exact diagonalization study of Mott transition in the Hubbard model on an anisotropic triangular lattice", ISSP International Workshop on Computational Approaches to Quantum Critical Phenomena, ISSP, Kashiwa, Japan (Aug. 2006)
2025 Autumn meeting
- Kaito Kobayashi and Yukitoshi Motome, "Enhanced performance of quantum reservoir computing at the edge of many-body quantum chaos"
- Kiyu Fukui and Yukitoshi Motome, "Unveiling diverse magnetic phases in extended Kitaev models on a three-dimensional hyperhoneycomb lattice"
- Shun Okumura, Moritz M. Hirschmann, and Yukitoshi Motome, "Spin-nodal lines and anomalous Hall effect induced by spin spirals"
- Rinsuke Yamada, Max T. Birch, Priya R. Baral, Shun Okumura, Ryota Nakano, Shang Gao, Masahiko Ezawa, Takuya Nomoto, Jan Masell, Yuki Ishihara, Kamil K. Kolincio, Ilya Belopolski, Hajime Sagayama, Hironori Nakao, Kazuki Ohishi, Takashi Ohhara, RYoji Kiyanagi, Taro Nakajima, Yoshinori Tojura, Takahisa Arima, Yukitoshi Motome, Moritz M. Hirschmann, and Max Hirschberger, "Discovery of a p-wave magnet with anisotropic transport properties"
- N. D. Khanh, H. Yoshimochi, M. Noda, S. Okumura, H. Kono, N. Matsuyama, A. Kitaori, S. Aji, H. Saito, H. Sagayama, S. Ito, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, R. Takagi, Y. Motome, T. Nakajima, S. Seki, "Resonant X-ray Scattering study of three-dimensional topological spin-textures in a centrosymmetric cubic magnet"
- Motofumi Noda, Haruto Yoshimochi, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Shun Okumura, Kono Hideki, Naofumi Matsuyama, Aki Kitaori, Seno Aji, Hiraku Saito, Hajime Sagayama, Shinichi Itoh, Satoru Hayami, Yasuyuki Kato, Rina Takagi, Yukitoshi Motome, Taro Nakajima, and Sinichiro Seki, "Emergent electrical transport in a rare-earth magnet hosting three-dimensional topological spin textures"
- Yasuyuki Kato, Takeshi Hayashida, Koei Matsumoto, Tsuyoshi Kimura, and Yukitoshi Motome, "Electric-field Induced Toroidal Moment in Antiferromagnetic Olivines"
- Midori Yamada, Shun Okumura, Kotaro Shimizu, Yasuyuki Kato, Yukitoshi Motome, "Monte Carlo study on magnetoelectric responses of magnetic monopoles in three-dimensional topological magnets"
- Aoi Kajihara, Shun Okumura, and Yukitoshi Motome, "Theoretical study on spin current generation via topological spin textures"
- Sogen Ikegami, Kiyu Fukui, Pohle Rico, and Yuktioshi Motome, "Higher-order spin interactions and multipole orders in S=3/2 quantum spin systems"
- Shoya Kasai, Kotaro Shimizu, Shun Okumura, and Yukitoshi Motome, "Stability and current-induced dynamics of a twist soliton on a magnetic skyrmion string"
2025 Spring meeting
- Shun Okumura, Moritz Hirschmann, and Yukitoshi Motome, "Theory of unconventional anomalous Hall effect induced by spin spirals論"
- Shoya Kasai, Shun Okumura, and Yukitoshi Motome, "Non-equilibrium dynamics of magnetic hopfions driven by spin-orbit torque"
- Kiyu Fukui and Yukitoshi Motome, "Ground-state phase diagram of the Kitaev-Γ model on a three-dimensional hyperhoneycomb lattice"
2024 Autumn meeting
- Y. Motome, "Quantum reservoir probing: exploring strongly correlated systems through information processing performance"
- S. Ikegami, K. Fukui, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Disorder and local topology on a Bishamon-kikko–honeycomb lattice"
- Y. Fujishiro, C. Terakura, A. Miyake, N. Kanazawa, K. Nakazawa, N. Ogawa, H. Kadobayashi, S. Kawaguchi, T. Kagayama, M. Tokunaga, Y. Kato, Y. Motome, K. Shimizu, and Y. Tokura, "Pressure-induced quantum phase transition and magneto-transport properties in chiral magnet FeGe"
- H. Fukuda, K. Ueda, C. Terakura, Y. Kaneko, Y. Fujishiro, S. Okumura, H. Saito, Y. Kato, M. Hirschberger, T. Nakajima, Y. Motome, and Y. Tokura, "Chiral spin liquid state and field-indiced topological Hall effect in pyrochlore Eu2Mo2O7"
- S. Wadashima and Y. Motome, "Spin glass-liquid transition in the extended Sachdev-Ye-Kitaev model"
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Motome, "Quantum reservoir probing of topological phase transitions"
2024 Spring meeting
- S. Hoshino, R. Pohle, and Y. Motome, "Derivation of a generalized LLG equation using electron-phonon coupling"
- K. Fukui and Y. Motome, "Topological Majorana flat bands in the Kitaev model on a Bishamon-kikko lattice"
- S. Ikegami, K. Fukui, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Topological phase diagram for the Haldane model on a Bishamon-kikko−honeycomb lattice"
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Motome, "Quantum reservoir probing of quantum phase transition"
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Motome. "Quantum reservoir probing of quantum information scrambling"
- S. Okumura, S. HayamiA, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Versatile magnetic hedgehog lattice phases and spin scalar chirality induced by anisotropic interactions in centrosymmetric systems"
- S. Kasai, K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Theoretical study of hopfion superstructures based on analysis of interactions between magnetic hopfions"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Current-induced dynamics and nonequilibrium topological phase transitions in an emergent magnetic monopole lattice"
2023 Autumn meeting
- L. Zhang and Y. Motome, "Ab initio study for heterostructures of a Kitaev magnet α-RuCl3 and CrX3 (X=Cl and I)"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Skin effect and edge states in the non-Hermitian Kitaev model in a magnetic field"
- Y. Kato, J. Nasu, T. Okubo, T. Misawa, M. Sato, and Y. Motome, "Spin Seebeck effect in the Kitaev spin liquid"
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Topological transitions by magnetization rotation in kagome monolayers of a ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal Co shandite"
- T. Nomura, Y. Kato, Y. Motome, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, Y. Kohama, S. Zherlitsyn, J. Wosnitza, S. Kimura, T. Katsuyoshi, T. Kimura, and K. Kimura, "High-field phase diagram of a chiral-lattice antiferromagnet Sr(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4"
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Motome, "Thermal robustness and spatiotemporal parallelization of physical reservoir computing in frustrated magnets"
- M. Naka, Y. Motome, T. Miyazaki, and H. Seo, "Piezomagnetic effect in κ-type organic compounds"
2023 Spring Meeting
- Y. Kato and Y. Motome, "Hidden topological transitions in emergent magnetic monopole lattices"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Topological transitions induced by a magnetic field in the non-Hermitian Kitaev model"
- S.-H. Jang and Y. Motome, "Theoretical investigation of Kitaev-type interactions for 4f electron systems"
- S.-H. Jang and Y. Motome, "Ab-initio study of crystal structures and electronic states for 4d-electron ilmenite metals ARuO3 (A=Mg, Cd)"
- T. Misawa, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Inter-edge spin resonance in the Kitaev spin liquid"
- R. Pohle, N. Shannon, Y. Motome, "Eight-color chiral spin liquid on a S=1 honeycomb Kitaev model with biquadratic interactions"
- Y. Shimizu, J. Yamamoto, Y. Kobayashi, T. Matsushita, T. Yamanaka, M. Kimata, T. Sasaki, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Anisotropy of spin excitations in α-RuCl3"
2022 Autumn meeting
- Y. Kato and Y. Motome, "Theoretical study on topological transition in three-dimensional magnetic hedgehog lattices"
- N. Mitsuishi, Y. Sugita, M. Kamitani, T. Akiba, M. Sakano, K. Horiba, H. Kumigashira, H. Sakai, H. Takahashi, S. Ishiwata, Y. Motome, and K. Ishizaka, "Investigation of structural instability in group-V transition metal tellurides MTe2 (M = V, Nb, Ta) from the viewpoint of electronic structures."
- Y. Otake, K. Inui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Improvement of deep neural networks by statistical mechanical analysis"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Edge effect on magnetic excitations in one-dimensional chiral magnets"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Edge effect on magnetic excitations in one-dimensional chiral magnets"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Emergent electric field around the edges of one-dimensional chiral magnets"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Ground-state phase diagram of the Kitaev-Heisenberg model on a three-dimensional hyperhoneycomb lattice"
- Rico Pohle, Nic Shannon, Yukitoshi Motome, "Possible chiral spin liquid on the spin-1 Kitaev-honeycomb model with bilinear-biquadratic interactions"
- K. Inui and Y. Motome, "Inverse design of Hamiltonian to maximize the photovoltaic effect using automatic differentiation"
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Magnetization-direction dependence of the Weyl state in atomically thin films of a ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal Co shandite"
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Layer number dependence of topological properties in atomically thin films of a ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal Co shandite"
77th Annual Meeting
- Y. Kato and Y. Motome, "Theoretical study on multiple-Q magnetic orderings and successive transitions induced by temperature and magnetic field"
- S. Hayami, T. Okubo, and Y. Motome, "Phase shift in skyrmion crystals"
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Theoretical analysis of the anomalous Hall effect in atomically thin films of a ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal Co3Sn2S2"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Theoretical study on the emergent electric field in one-dimensional chiral magnets"
- M. Kamimura, M. Shimomura, Y. Ukai, S. Suetsugu, T. Asaba, Y. Kasahara, N. KuritaA, H. Tanaka, T. Shibauchi, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, and Y. Matsuda, "Field-induced topological phase transition in a Kitaev spin liquid candidate α-RuCl3"
- R. Pohle, N. Shannon, and Y. Motome, "Spin liquid and nematic states in the spin-1 honeycomb Kitaev model with bilinear-biquadratic interactions"
- K. Inui and Y. Motome, "Automatic design of Hamiltonians with nontrivial topological properties by exploiting machine learning"
2021 Autumn meeting
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Ab initio calculation of thin films of a ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal Co3Sn2S2: structural optimization and effective model analysis"
- Y. Shimizu, J. Yamamoto, K. Yoshiaki, T. Matsushita, M. Itoh, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Anisotropy spin of excitations in α-RuCl3"
- K. Inui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Fermionic many-body wavefunction using determinant-implemented convolutional neural network"
- K. Inui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Determinant-free fermionic many-body wavefunction using feed-forward neural networks"
- N. D. Khanh, T. Nakajima, S. Hayami, S. Gao, Y. Yamasaki, H. Sagayama, H. Nakao, R. Takagi, Y. Motome, Y. Tokura, T. Arima, S. Seki, "Multiple-Q spin textures in tetragonal itinerant magnet GdRu2Si2"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Topological phase transition associated with phase degree of freedomin three-dimensional multiple-Q spin textures"
- Y. Kato and Y. Motome, "Model analysis for multiple-Q magnetic orderings: magnetic field-temperature phase diagrams"
- S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic field dependence of the helical plane and ellipticity in multiple-Q magnetic textures in a centrosymmetric system"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, J Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Ground state phase diagrams of spin S>1/2 Kitaev-Heisenberg model"
- M. Naka, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, "Anomalous Hall effect in perovskite antiferromagnets"
76th Annual Meeting
- S.-H. Jang and ○Y. Motome, "Electronic and magnetic properties of honeycomb-lattice ilmenite iridates MIrO3 (M=Mg, Zn, Mn)"
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Thermal transport in the Kitaev spin liquid under staggered magnetic fields"
- S.-H. Jang, Y, Kato, and Y. Motome, "Creation and control of anyons in a Kitaev spin liquid by local perturbations"
- T. Okubo, J. Nasu, T. Misawa, and Y. Motome, "Effect of off-diagonal exchange interactions on the thermal Hall conductivity of the Kitaev spin liquid"
- S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic hedgehog lattices in centrosymmetric metals"
- K. Inui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Approximate fermion many-body wave function by a feed-forward neural network"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "On the realization of Kitaev quantum spin liquid in ultracold polar molecule systems: functional renormalization group study"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Phason in multiple-Q topological spin textures"
- Y. Kato, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, "Spin-wave excitation in multiple-Q magnetic orderings"
2020 Autumn meeting
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Spin Moire engineering of emergent electromagnetism and topological transitions"
- S. Okumura, T. Morimoto, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Numerical study on the electric magnetochiral effect in a conical magnetic metal"
- K. Kimura, Y. Kato, S. Kimura, Y. Motome, and T. Kimura, "Crystal-chirality-dependent magnetoelectric response in the antiferromagnetic phase of Pb(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4"
- T. Yokoi, S. Ma, Y. Kasahara, S.Kasahara, T. Shibauchi, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, C. Hickey, S. Trebst, and Y. Matsuda, "Half-integer quantized anomalous thermal Hall effect in Kitaev spin liquidα-RuCl3"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, "Disorder effect on dynamics of the Kitaev spin liquid"
- N. Mitsuishi, Y. Sugita, T. Akiba, Y. Takahashi, S. Yoshida, S. B. Kenichi, M. Sakano, R. Yukawa, K. Horiba, H. Kumigashira, K. Miyamoto, T. Okuda, H. Takahashi, S. Ishiwata, Y. Motome, and K. Ishizaka, "Electronic structure of CDW material TaTe2 with tantalum double zigzag chains to heptamers"
- H. Yasuda, Y. Kato, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, "First-principles analysis of spin-orbital coupled phenomena in a pyrochlore oxideCd2Re2O7"
- Y. Yasui, C. J. Butler, N. D. Khanh, S. Hayami, T. Nomoto, T. Hanaguri, Y. Motome, R. Arita, T. Arima, Y. Tokura, and S. Seki"Relation between electronic-state modulations and magnetic structures in the magnetic skyrmion compound GdRu2Si2"
- K. Inui and Y. Motome, "Channel-selective non-Fermi liquid and heavy fermion behavior in a two-channel Kondo lattice model under a magnetic field"
- M. Naka, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, "Perovskite oxides as a spin current generator"
- S. Okumura, T. Morimoto, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Numerical study on nonlinear optical responses in a conical magnetic state"
- S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Field-induced topological transitions in magnetic hedgehog lattices in itinerant magnets"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Phase transitions between helices, vortices, and hedgehogs in chiral magnets driven by spatial anisotropy"
- T. Nomura, Y. Kato, Y. Motome, S. Zherlitsyn, Y. Kohama, T. Katsuyoshi, T. Kimura, and K. Kimura, "Elastic properties and magnetocaloric effect of Sr(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4 under high magnetic fields"
75th Annual Meeting (2019)
- M. Naka, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, "Spin splitting and spin current generation in perovskite oxides"
- S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, " Numerical study of the field effects on magnetic hedgehog lattices in itinerant magnets"
- K. Inui, J. Yoshitake, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic phase diagram and specific heat calculation for a two-channel Kondo lattice model: cluster DMFT study"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, "Disorder effect on the Kitaev spin liquid"
- Y. Shimizu, Y. Nagai, T. Jinno, M. Itoh, J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Anisotropy of magnetic excitations in Kitaev quantum spin liquid candidateα-RuCl3"
- Khanh Nguyen, Taro Nakajima, Satoru Hayami, Shang Gao, Hironori Nakao, Hajime Sagayama, Yuichi Yamasaki, Yukitoshi Motome, Yoshinori Tokura, Takahisa Arima, Shinichiro Seki, "Multiple-Q spin textures in itinerant magnet GdRu2Si2"
- T. Yokoi, S. Ma, Y. Kasahara, S.Kasahara, T. Shibauchi , N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, C. Hickey, S. Trebst, and Y. Matsuda, "Field angular variation of Chern number in Kitaev spin liquid α-RuCl3"
- H. Yasuda, Y. Kato, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, "First-principles calculation for the magneto-current effect in a pyrochlore oxideCd2Re2O7"
2019 Autumn meeting
- K. N. Okada, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Magnetoelectric effect in band insulator-ferromagnet heterostructures"
- M. Naka, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, Y. Yanagi, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, "Anomalous Hall effect in κ-type molecular conductors"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, "Resonant Majorana excitations by AC magnetic field in Kitaev spin liquids"
- T. Tominaga, T. Yokoi, S. Ma, Y. Kasahara, Y. Sato, H. Murayama, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, C. Hickey, S. Trebst, C. Lee, K.-Y. Song, T. Shibauchi, and Y. Matsuda, "Thermal transport and Ir substitution effect in α-RuCl3"
- Y. Kato and Y. Motome, "Theoretical study of magnetic excitation in antiferromagnetic square cupola systems A(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4"
- S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Numerical study on multiple-Q magnetic hedgehog lattices in 3D itinerant electron systems"
74th Annual Meeting (2019)
- Y. Kato, K. Kimura, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, A. Matsuo, K. Kindo, M. Akaki, M. Hagiwara, S. Kimura, T. Kimura, and Y. Motome, "Magnetization curve and magnetoelectric effect in antiferromagnetic square cupolas (A(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4, A = Sr): comparison with isostructurals (A = Ba and Pb)"
- S. Ma, Y. Kasahara, T. Onishi, Y. Mizukami, O. Tanaka, K. Sugii, M. Shimozawa, M. Yamashita, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, T. Shibauchi、 and Y. Matsuda, "Field-angle dependence of thermal Hall effect in α-RuCl3"
- Y. Sugita and Y. Motome, "Antiferromagnetic Kitaev-type interactions in polar spin-orbit Mott insulators"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, "Spin dynamics of the Kitaev model in a magnetic field"
- S.-H. Jang, R. Sano, Y, Kato, and Y. Motome, "Rare-earth materials research for Kitaev spin liquids"
- M. Oono, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Magnetoelectric effect in spin-1/2 quantum breathing pyrochlore systems"
- N. Mitsuishi, Y. Takahashi, Y. Sugita, T. Akiba, M. Sakano, R, Yukawa, K. Horiba, H. Kumigashira, S. Ishiwata, Y. Motome, and K. Ishizaka, "Electronic structure of TaTe2 showing CDW transition with double zigzag chains to heptamers II"
- M. Naka, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, Y. Yanagi, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, "Symmetry breaking and transport properties in κ-type molecular conductors"
- P. Mishchenko, Y. Kato, K. O’Brien, T. Bojesen, T. Eschmann, M. Hermanns, S. Trebst, and Y. Motome, "Chiral spin liquids in the Kitaev model on a three-dimensional hypernonagon lattice"
2018 Autumn Meeting
- Y. Sugita and Y. Motome, "Spin-orbit physics in honeycomb-layered transition metal compounds with mixed anions"
- Y. Sugita and Y. Motome, "Two-dimensional band crossings and topological band structures of eg-orbital electrons in honeycomb structures"
- S. Ma, Y. Kasahara, T. Onishi, Y. Mizukami, O. Tanaka, K. Sugii, M. Shimozawa, M. Yamashita, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, T. Shibauchi, and Y. Matsuda, "Verification of Majorana quantization conditions inα-RuCl3"
- M. Naka, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, Y. Yanagi, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, "Spin current generation in κ-type molecular conductors"
- M. Naka, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, Y. Yanagi, Y. Motome, and H. Seo, "Spin splitting in κ-type molecular conductors"
- M. Onga, Y. Sugita, T. Ideue, Y. Nakagawa, R. Suzuki, Y. Motome, andY. Iwasa, "Optical properties of magnetic van der Waals heterointerfaces"
- N. Mitsuishi, Y. Sugita, T. Akiba, M. Sakano, K. Horiba, H. Kumigashira, S. Ishiwata, Y. Motome, and K. Ishizaka, "Electronic structure of TaTe2 showing CDW transition with double zigzag chains to heptamers"
- S. Okumura, H. Ishizuka, Y. Kato, J. Ohe, and Y. Motome, "Numerical study on nonreciprocal spin current in conical magnetic states"
- Y. Motome (Symposium talk), "Magnetic excitations in Kitaev magnets"
- S.-H. Jang, R. Sano, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Material design of Kitaev spin liquids: possible realization of antiferromagnetic Kitaev interactions"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, "Non-equilibrium dynamics by field quench in Kitaev model"
- J. Nasu, Y. Kato, Y. Kamiya, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic-field driven topological transitions in Kitaev spin liquid"
- Y. Yanagi, S. Hayami, Y. Motome, and H. Kusunose, "Multipole ordering and nonreciprocal response in Cd2Re2O7"
- S. Hayami, Y. Yanagi, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Possibility of electric toroidal quadrupole ordering in Cd2Re2O7"
73rd Annual Meeting (2018)
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Odd-parity multipoles and magnetoelectric effects in 5d transition metal oxides AOsO4 (A=K, Rb, Cs)"
- Y. Sugita and Y. Motome, "Material design of exotic 2D band structures in honeycomb-layered transition metal compounds"
- S. Ma, Y. Kasahara, T. Onishi, K. Sugii, M. Shimozawa, M. Yamashita, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, T. Shibauchi, and Y. Matsuda, "Observation of half-integer thermal Hall effect in a Kitaev spin-liquid"
- N. Mitsuishi, Y. Sugita, M. Kamitani, T. Sonobe, M. Sakano, T. Shimojima, M. S. Bahramy, K. Horiba, H. Kumigashira, K. Taguchi, K. Miyamoto, T. Okuda, S. Ishiwata, Y. Motome, and K. Ishizaka, "Electronic structure of 1T”-VTe2 with double-zigzag chain shape lattice distortion"
- Y. Kato, Y. Kamiya, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Ground state analysis of the hypernonagon Kitaev model"
- Y. Motome (Symposium talk), "Theory of Kitaev spin liquids: toward the observation of Majorana particles"
- S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Commensurate locking of a chiral soliton lattice by itinerant electrons"
- R. Takashima, Y. Shiomi, and Y. Motome, "Nonreciprocal spin Seebeck effect in antiferromagnet"
2017 Autumn Meeting
- Y. Sugita, T. Miyake, and Y. Motome, "Multiple Dirac cones from geometrical and orbital natures of transition metal trichalcogenides"
- M. Naka, H. Seo, and Y. Motome, "Theory of spin and charge ordering with valence transition in A-site ordered perovskite transition-metal oxides"
- Y. Kato and Y. Motome, "Theoretical study of magnetoelectric effect in ferroelectric square cupolas"
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, "Multiple-Q magnetic orderings in the Kondo lattice model with the spin-orbit coupling"
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, "Effect of magnetic anisotropy on skyrmion crystal in the Kondo lattice model"
- R. Takashima, Y. Kato, Y. Yanase, and Y. Motome, "Noncollinear magnetic order induced by superconducting current"
- K. N. Okada, R. Ozawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Multiple-Q magnetic order induced by Rashba-Dresselhaus spin-orbit couplings"
- Y. Kato, Y. Kamiya, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Finite-temperature phase transition to three-dimensional chiral spin liquids: Monte Carlo study of anisotropic limits of hypernonagon Kitaev model"
- J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Temperature evolution of spin dynamics in two- and three-dimensional Kitaev models: Influence of fluctuating gauge fluxes"
- J. Nasu, J. Yoshitake, Y. Kamiya, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic field effect on Kitaev spin liquids"
- Y. Kamiya, J. Yoshitake, Y. Kato, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Emergent fluxes and linear and nonlinear magnetic responses in the gapped Kitaev quantum spin liquid: different behaviors between the ferromagnetic and the antiferromagnetic cases"
- T. OnishiA, K. Sugii, M. Shimozawa, M. Yamashita, Y. Tokiwa, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, T. Shibauchi, Y. Kasahara, and Y. Matsuda "A signature of Majorana chiral edge current in a Kitaev spin-liquid: α-RuCl3"
- Y. Nagai, Y. Shimizu, M. Itoh, J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic-field-induced phase transition in a Kitaev-type honeycomb antiferromagnet α-RuCl3"
- S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Impact of itinerant electrons on magnetic-field dependence of chiral soliton lattice"
- R. Sano, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Kitaev-Heisenberg Hamiltonian for High-Spin d7 Mott Insulators"
72nd Annual Meeting (2017)
- J. Nasu, J. Yoshitake, and Y. Motome, "Thermal transport phenomena in the Kitaev model"
- J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Effect of magnetic field in the Kitaev model: NMR relaxation rate and nonlinear susceptibility"
- Y. Sugita, T. Miyake, and Y. Motome, "Dirac cones and electron correlations in transition metal trichalcogenides"
- A. Oyamada, E. Yamamoto, Y. Haga, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Anomalous Hall effect in a triangular-lattice antiferromagnet UNi4B"
- S. Okumura, Y. Kato and Y. Motome, "Numerical study of a chiral soliton lattice in a monoaxial magnetic conductor"
- Y. Nagai, Y. Shimizu, M. Itoh, J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "35Cl NMR in a Kitaev-type honeycomb antiferromagnet α-RuCl3"
- S. Hayami, R. Ozawa, and Y. Motome, "Skyrmion crystal phases induced by effective spin-spin interactions in the Kondo lattice model"
- R. Ozawa, Y. Kato, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, "Temperature-field phase diagram of skyrmion crystals with different topological numbers in the Kondo lattice model"
- Y. Kato, K. Kimura, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, A. Matsuo, K. Kindo, M. Akaki, M. Hagiwara, M. Sera, T. Kimura, and Y. Motome, "Multipole decomposition and magnetoelectric behavior in square cupola systems"
- P. A. Mishchenko, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Large-Scale Simulation of “Liquid-Gas” Phase Transition in the Kitaev Model on a Hyperoctagon Lattice"
2016 Autumn Meeting
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Emergent spin-valley-orbital physics by spontaneous parity breaking"
- Y. Kato, K. Kimura, A. Miyake, M. Tokunaga, A. Matsuo, K. Kindo, M. Akaki, M. Hagiwara, M. Sera, T. Kimura, and Y. Motome, "Magnetization Curve and Magnetoelectric Effect in Antiferromagnetic Chiral Square Cupolas (A(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4(A=Ba, Sr))"
- K. Yamauchi, H. Seo, M. Naka, and Y. Motome, "Ab initio density functional theory calculation of BiMO3 (M:3d transition metal)"
- M. Naka, H. Seo, and Y. Motome, "Theory of valence transition in perovskite transition-metal oxides including valence skipping elements"
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, "Thermal Hall effect in an applied magnetic field in a Kitaev model"
- J. Nasu, J. Knolle, D.L. Kovrizhin, Y. Motome, and R. Moessner, "Fermionic response from fractionalization in a Kitaev model: comparison with the Raman scattering experiment in α-RuCl3"
- Y. Nagai, Y. Shimizu, M. Itoh, J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, "35Cl NMR in a Kitaev-type honeycomb antiferromagnet α-RuCl3"
- R. Ozawa, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, "Domain structure of multiple-Q ordered states in itinerant magnets"
- R. Ozawa, C. D. Batista, and Y. Motome, "Skyrmion crystals induced by spin-charge coupling"
- R. Ozawa, K. Barros, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, "Collinear, coplanar, and noncoplanar magnetic transitions induced by the magnetic anisotropy and external magnetic field in spin-charge coupled systems"
71st Annual Meeting (2016)
- A. Oyamada, E. Yamamoto, Y. Haga, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Weak ferromagnetism and anomalous Hall effect in a triangular-lattice antiferromagnet UNi4B"
- J. Nasu, J. Yoshitake, Y. Kato, Y. Kamiya, Y. Motome, "A liquid-liquid transition in an extended Kitaev model by including Ising interactions"
- K. Inui, J. Yoshitake, and Y. Motome, "Crossover Behavior in the Magnetic Phase Diagram of Quadrupolar Kondo Lattice Systems"
- Y. Sugita and Y. Motome, "Spin and valley physics induced by charge order on a triangular lattice"
- J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic fluctuations and dynamics in the vicinity of Kitaev quantum spin liquids"
2015 Autumn Meeting
- K. Inui, J. Yoshitake, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic phase diagram for a two-channel Kondo lattice model: cluster DMFT study"
- Y. Kato and T. Misawa, "Quantum Tricriticality in Transverse field Ising Model: A Quantum Monte-Carlo Study"
- A. Oyamada, E. Yamamoto, Y. Haga, S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Anomalous Hall effect in the magnetically ordered state in a triangular-lattice antiferromagnet UNi4B"
- J. Yoshitake and Y. Motome, "Cluster dynamical mean-field study of the Kitaev model"
- J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, Y. Motome, J. Knolle, D. Kovrizhin, and R. Moessner, "Dynamical magnetic response in the Kitaev model at finite temperature"
- Y. Akagi and Y. Motome, "Magnetic phase diagram in spin-charge coupled system: Kagome network and supersolid phases"
- S. Hayami, R. Ozawa, Y. Motome, and C. D. Batista, "Stabilizing Mechanism of Meron Crystals: Weak Coupling Approach"
- R. Ozawa, K. Barros, S. Hayami, G-W. Chern, M. Udagawa, Y. Motome, and C. D. Batista, "Numerical Study on Meron Crystals with Spin Scalar Chiral Stripes on a Square Lattice"
70th Annual Meeting (2015)
- M. Naka, H. Seo, and Y. Motome, "Theory of intermetallic charge transfer and insulator-metal transition in BiNiO3 showing colossal negative thermal expansion"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Collective Excitations in Toroidal Ordered Systems"
- Y. Sugita, S. Hayami, and Y. Motome, "Orbital order and anomalous electronic state in a d-p model with parity mixing"
- A. Uehara, H. Shinaoka, and Y. Motome, "RPA analysis of the generalized susceptibility for charge-spin-orbital fluctuations in mixed-valence spinels"
- J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Finite-temperature phase transition in a chiral spin liquid"
- R. Ozawa, M. Udagawa, Y. Motome, K. Barros, G-W. Chern, and C. D. Batista, "Spin Scalar Chiral Stripes in the Kondo Lattice Model on a Square Lattice"
- H. Sanjo and Y. Motome, "Theoretical study on the effects of randomness and electron-electron correlation in quasi-periodic systems"
- Y. Motome, "Introduction", Division 8, 3 Symposium, "New horizon of spin-orbit physics - Novel properties emergent from Kitaev-type anisotropic interactions"
- Y. Kamiya, Y. Kato, J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Quantum Monte Carlo study of a spin liquid: a liquid-solid transition in the perturbed toric code in d=2, 3"
- M. Udagawa, "(Young Scientist Award of the Physical Society of Japan) Theoretical study of itinerant electron systems with strong geometrical frustration"
2014 Autumn Meeting
- J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Thermodynamic properties and gap structure in the Kitaev model"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic ordering in an extended Kondo lattice model with local parity mixing"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Spontaneous parity breaking in spin-orbital coupled systems"
- S. Hayami and Y. Motome, "A stabilization mechanism of noncollinear and noncoplanar magnetic ordering"
- A. Uehara, H. Shinaoka, and Y. Motome, "Spin-orbit coupling and crystal field splitting in spinel oxides: RPA analysis of generalized susceptibilities"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Current-driven domain wall creation in All-in/All-out magnets"
- J. Nasu, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Finite-temperature phase transition to quantum spin liquids in a three-dimensional Kitaev model"
69th Annual Meeting (2014)
- J. Nasu and Y. Motome, "Exotic Magnetic State due to Spin-orbit Coupling in an Octamer Phase of Spinel Compound CuIr2S4"
- J. Nasu, T. Kaji, K. Matsuura, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Change of Magnetic State associated with Finite-Temperature Phase Transition in a 3D Kitaev Model"
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Toroidal ordering in metals: band shift, magnetotransport, and magnetoelectric effect"
- Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, Y. Motome, "Magnon Hall Effect in a Kondo Lattice System"
2013 Autumn Meeting
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Motome, T. Miyake, and S. Ishibashi, "Spin-orbital frustration in molybdenum pyrochlores"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, "Loop Liquid State in an Ising-Spin Kondo Lattice Model on a Kagome Lattice"
- R. Ozawa, Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Surface effects in a scalar chiral ordered phase: real-space analysis on the reconstruction of edge states"
- S. Hayami, T. Misawa, Y. Yamaji, and Y. Motome, "Monte Carlo analysis for multiple-Q magnetic order in a cubic classical Kondo lattice model"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Magnetic and Transport Properties in the All-in/All-out Phase of Pyrochlore Conductors"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Ground-state properties of the Hubbard model on line graphs in the strong coupling limit"
- J. Nasu, T. Kaji, K. Matsuura, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Nontrivial Finite-Temperature Phase Transition in a 3D Kitaev Model"
68th Annual Meeting (2013)
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, "Spontaneous Inversion Symmetry Breaking in Spin Ice Double-Exchange Model"
- Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Quantum Fluctuation Effect on a Spin Scalar Chiral Ordering in a Kondo Lattice System"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Charge-spin correlation at strong coupling limit of frustrated Hubbard model"
- R. Ozawa, Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Reconstruction of edge states in a two-dimensional spin-scalar-chiral phase"
- S. Hayami, T. Misawa, Y. Yamaji, and Y. Motome, "Noncoplanar multiple-Q magnetic order with three-dimensional Dirac electrons on a cubic lattice
2012 Autumn Meeting
- S. Hayami, T. Misawa, and Y. Motome, "Multiple-Q magnetic order and charge order in the periodic Anderson model"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, "Spin-ice type Liquid State and Anomalous Hall Effect in Kagome Lattice Double- exchange Model"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, "Charge order and electronic structure of partially disordered states in a Kondo lattice model on a triangular lattice"
- K. Inui, H. Ishizuka, and Y. Motome "Spin chirality ordering induced by external magnetic field in the Hubbard model on a kagome lattice"
- M. Udagawa and R. Moessner, "Anomalous Hall effect driven by spatially inhomogeneous spin structure in frustrated conduction systems"
- M. Udagawa and R. Moessner, "Anomalous Hall effect driven by spatially inhomogeneous spin structure in frustrated conduction systems"
- M. Udagawa, H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome "Transport phenomena and dynamical response of spin ice conduction systems"
- S. Hayami, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome "Partial disorder induced by magnetic field and spin anisotropy in the periodic Anderson model on a triangular lattice"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, "Dirac Half-metal in a Triangular Ferrimagnet"
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic excitations of spin-glass phase in Heisenberg antiferromagnets coupled with local lattice distortions on a pyrochlore lattice"
67th Annual Meeting (2012)
- J. Yoshitake, T. Misawa, and Y. Motome, "Charge ordering in the Kondo lattice model at quarter filling"
- S. Hayami, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Partial disorder at commensurate fillings in the periodic Anderson model on a triangular lattice"
- Y. Motome, "Higher-order and multiple degrees of freedom in correlated electron systems -Novel quantum states and transport properties-", Division 8, 3, 7 Symposium, "Strongly-correlated condensed-matter science opened up by new materials"
- Y. Akagi and Y. motome, "Spontaneous kagome-network formation in the ferromagnetic Kondo-lattice model on the triangular lattice"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, "Partially disordered state in an Ising-spin Kondo lattice model on a triangular lattice"
2011 Autumn Meeting
- A. Miyata, H. Sawabe, Y. Matsuda, H. Ueda, Y. Ueda, Y. Motome, N. Shannon, K. Penc, and S. Takeyama, "Magnetization of highly frustrated chromium spinel oxides in ultra-high magnetic field II"
- S. Hayami, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Partial disorder in the periodic Anderson model on a frustrated lattice"
- M. Udagawa, H. Ishizuka, and Y. Motome, "Non-Kondo resistivity minimum in spin ice itinerant systems"
- H. Ishizuka, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic ordering and spin liquid in an Ising spin Kondo lattice model on a pyrochlore lattice"
- Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Spin-chirality ordering and kinetic-driven effective interactions in geometrically-frustrated ferromagnetic Kondo-lattice systems"
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, "Spin-glass transition in bond-disordered Heisenberg antiferromagnets coupled with local lattice distortions on a pyrochlore lattice"
66th Annual Meeting (2011)
- S. Sakai, G. Sangiovanni, M. Civelli, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, "System-size dependence in the cluster dynamical mean-field theory"
- Y. Akagi and Y. Motome, "Spin-chirality ordering and its stabilization mechanism in geometrically-frustrated ferromagnetic Kondo-lattice systems"
- M. Udagawa, H. Ishizuka, and Y. Motome, "Electronic and Conduction properties of spin ice itinerant systems"
- H. Ishizuka, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Monte Carlo study of itinerant spin-ice models on a pyrochlore lattice"
- S. Hayami, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Partial Kondo screening formation in frustrated periodic Anderson model"
- A. Miyata, H. Sawabe, Y. Matsuda, H. Ueda, Y. Ueda, Y. Motome, N. Shannon, K. Penc, and S. Takeyama, "Magnetization of highly frustrated chromium spinel oxides in ultra-high magnetic field"
2010 Autumn Meeting
- H. Shinaoka, Y. Tomita, and Y. Motome, "Spin multipole ordering and spin glass transition in pyrochlore oxides R2Mo2O7"
- A. Miyata, H. Sawabe, Y. Matsuda, S. Takeyama, H. Ueda, H. Ueda, Y. Motome, N. Shannon, and K. Penc, "Investigation of magnetic phases of ZnCr2O4 up to 600T using the electro-magnetic flux compression method"
- H. Ishizuka, Y. Motome, N. Furukawa, and S. Suzuki, "Antiferroelectric-Paraelectric Transition of Squaric Acid Crystals: Effects of Geometrical Frustration and Quantum Fluctuations"
- S. Okumura, H. Kawamura, T. Okubo, and Y. Motome, "Novel spin liquids in Heisenberg antiferromagnets on a honeycomb lattice"
- T. Misawa and Y. Motome, "Dimensional reduction and novel orderings in anisotropic antiferro-magnetic Heisenberg models on a stacked kagome lattice"
- Y. Akagi and Y. Motome, "Spin-chirality ordering and anomaluos Hall effect in the two dimen- sional geometrically-frustrated ferromagnetic Kondo-lattice system"
- J. Yoshitake and Y. Motome, "Trimer formation and Metal-Insulator transition in the triangular lattice systems LiVX2 (X=O,S,Se)"
- H. Ishizuka, Y. Motome, N. Furukawa, and S. Suzuki, "Effect of quantum fluctuation in frustrated extended-Ising models on a checkerboard lattice"
- H. Ishizuka, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Transport Properties and Dimensionality of Itinerant Electrons Coupled to Charge Frustrated Systems"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Magnetic order and electronic state of itinerant electron systems coupled to spin ice"
- S. Sakai, Giorgio Sangiovanni, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, "s-wave pseudogap in the 2-dimensional Hubbard model"
- M. Udagawa, H. Ishizuka, and Y. Motome, "Excited states of frustrated itinerant electrons: Monopole excitation and fractional charge in the charge ice phase"
- H. Shinaoka and Y. Motome, "Loop algorithm for classical Heisenberg models with spin-ice type degeneracy"
65th Annual Meeting (2010)
- Y. Otsuka, H. Seo, and Y. Motome, "Finite-temperature phase diagram of 1D π-d System"
- H. Ishizuka, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Local constraint and Electronic Structure in Charge Frustrated Systems"
- M. Udagawa, H. Ishizuka, and Y. Motome, "Anomalous properties of frustrated itinerant systems: Effect of coupling to a system under the “ice rule” local constraint"
- J. Yoshitake and Y. Motome, "Relaxation of frustration by cluster formation in multi-orbital systems"
- Y. Akagi and Y. Motome, "Spin-chirality ordering and anomaluos Hall effect in the ferromagnetic Kondo-lattice model on the triangular lattice"
- K. Nakamikawa, Y. Yamaji, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Variational Monte Carlo Study of Partial Kondo Screening in Kondo Lattice Systems"
- S. Okumura, H. Kawamura, and Y. Motome, "Order from disorder in the Ordering of the classical J1-J2 model on the honeycomb lattice"
2009 Autumn Meeting
- Y. Otsuka, H. Seo, and Y. Motome, "Charge Order and Finite-Temperature Properties in the 1D π-d System"
- S. Sakai, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, "Theory of Fermi arc incorporating zeros of Green’s function"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa "Phase Competition and Phase Separation in Double-Exchange Model on the Pyrochlore Lattice "
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Chirality and heavy-quasipar ticle formation in the Hubbard model on kagome lattice"
- Y. Motome, K, Penc, and N. Shannon, "Quadrupolar and Octupolar Orderings in the Pyrochlore Antiferromagnets with Biquadratic Interaction"
- A. Miyata, E. Kojima, H. Ueda, Y. Ueda, Y. Motome, and S. Takeyama, "Magnetization process of frustrated chromium spinel oxide ZnCr2O4 in ultra-high magnetic fields, III"
64th Annual Meeting (2009)
- S. Sakai, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, "Reconstruction of poles and zeros of Green's function in Mott transiton"
- H. Uchigaito, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Competition among charge, spin, and orbital states and metal-insulator transition in triangular-lattice systems ANiO2"
- A. Miyata, E. Kojima, H. Ueda, H. Ueda, S. Takeyama, and Y. Motome, "Magnetization process under megagauss field of frustrated spinel oxide ZnCr2O4 II"
- M. Azuma, O. Smirnova, Y. Simakawa, N. Kumada, M. Matsuda, M. Tokunaga, and Y. Motome, "Frustrated honeycomb compound with S=3/2, Bi3Mn4O12(NO3)"
- T. Misawa and Y. Motome, "Non-equilibrium relaxation study of chiral and KT transitions in anisotropic Heisenberg model on the triangular lattice"
2008 Autumn Meeting
- Y. Motome, "Origin of Metal-Insulator Transition and Trimer Formation in Triangular-Lattice Systems LiVX2 (X=O,S)"
- S. Sakai, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, "Non-Fermi liquid and zeros of Green's function in the vicinity of Mott insulator"
- H. Uchigaito, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Frustration and competition among charge, spin and orbital degrees of freedom in triangular-lattice compounds ANiO2 (A=Na,Li,Ag)"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Magnetic fluctuations of the Hubbard model on frustrated lattices in strongly-correlated regime"
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, "Numerical Study of Double-Exchange Model on the Pyrochlore Lattice"
63rd Annual Meeting (2008)
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Spin fluctuation and correlation effects in the Hubbard model on kagome and hyperkagome lattices"
- S. Sakai, Y. Motome, and M. Imada, "Zeros of Green's function and anomalous metals in the vicinity of Mott insulator"
- H. Seo and Y. Motome "Charge frustration and novel electron-lattice coupled ordering in DI-DCNQI2Ag"
62nd Annual Meeting (2007)
- Y. Otsuka, H. Seo, T. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Numerical study of finite-temperature phase transitions and physical properties of quasi-one-dimensional molecular conductors"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Analysis of non-equilibrium steady states in an applied electric field in charge-ordered systems"
2007 Spring Meeting
- Y. Motome, "Comment", Division 8 Symposium "Frustration and Anomalous Quantum Phase in Orbitally-degenerate Systems"
2006 Autumn Meeting
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Suppression of horizontal charge ordering and coexistence of charge fluctuations with different wave numbers in theta-type ET salts"
- H. Seo, T. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Numerical study on electron-lattice coupled properties of quasi-one-dimensional molecular conductors"
- T. Koretsune, Y. Motome, and A. Furusaki, "Metal-insulator transition and magnetic ordering in the Hubbard model on an anisotropic triangular lattice"
84th JSAP Autumn Meeting 2023
- K. Fujiwara, Y. Kato, H. Abe, S. Noguchi, J. Shiogai, Y. Niwa, H. Kumigashira, Y. Motome, A. Tsukazaki, "Topological aspects of the anomalous transport phenomena in amorphous Fe–Sn thin films"
- 小林海翔, 求 幸年, "量子リザバープロービングによる情報の非局在化過程の解析"
70th JSAP Spring Meeting 2023
- 小林海翔, 求 幸年, "磁性体を用いたリザバーコンピューティングの熱的堅牢性と並列化"
2025 (Anaheim, California)
- M. Hirschberger, T. Arima, P. R. Baral, M. Birch, S. Gao, M. M. Hirschmann, Y. Ishihara, K. K Kolincio, Y. Motome, T. Nakajima, R. Nakano, H. Nakao, K. Ohishi, S. Okumura, H. Sagayama, Y. Tokura, and R. Yamada, "Discovery and synthesis of a p-wave magnet with a giant anomalous Hall susceptibility"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Zero-to-Perfect Toron Hall Effect in Chiral Magnets"
- H. Fukuda, Y. Fujishiro, M. Hirschberger, Y. Kaneko, Y. Kato, Y. Motome, T. Nakajima, S. Okumura, H. Saito, C. Terakura, Y. Tokura, and K. Ueda, "Non-Fermi liquid state and field-induced topological Hall effect in pyrochlore-type Eu2Mo2O7"
- N. Shannon, Y. Akagi, Y. Amari, O. Benton, L. Chojnacki, Y. Motome, R. Pohle, G. Rakala, K. Remund, J. Romhanyi, and H. Yan, "Simulation of spin-1 magnets on frustrated lattices"
2024 (Minneapolis, Minnesota)
- K. Inui and Y. Motome, "Inverse Hamiltonian design of highly-entangled quantum many-body systems"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Effect of a magnetic field on the Kitaev model coupled to environment"
- L. Zhang and Y. Motome, "Ab initio study for heterostructures of a Kitaev magnet α-RuCl3 and CrX3 (X=Cl and I)"
- Y.-F. Zhao, S.-H. Jang, and Y. Motome, "Spin-orbit coupled insulators and metals on the verge of Kitaev spin liquids in ilmenite heterostructures"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Emergent electric field and resonance dynamics in a one-dimensional chiral magnet driven by an AC magnetic field"
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Motome, "Quantum reservoir probing of information propagation and scrambling"
- Y. Kato, J. Nasu, M. Sato, T. Okubo, T. Misawa, and Y. Motome, "Spin Seebeck effect in the Kitaev spin liquid"
2023 (Las Vegas, Nevada)
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Layer number dependence of topological properties in atomically thin films of a ferromagnetic Weyl semimetal Co-based shandite"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Phase degree of freedom and topological properties of multiple-Q spin textures"
- K. Inui and Y. Motome, "Inverse Hamiltonian design by automatic differentiation"
2022 (Chicago, Illinois/hybrid)
- Y. Kasahara, S. Suetsugu, Y. Ukai, M. Shimomura, H. Murayama, T. Asaba, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, Y. Mizukami, K. Hashimoto, T. Shibauchi, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, and Y. Matsuda, "Thermodynamic evidence for a topological phase transition in a spin liquid state of α-RuCl3"
- K. Inui, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Determinant-free fermionic wave function using feed-forward neural networks"
- K. Nakazawa, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Thermal transport in the Kitaev spin liquid under a staggered magnetic field"
- S. Suetsugu, U. Yuzuki, M. Shimomura, Y. Kasahara, H. Murayama, T. Asaba, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, Y. Mizukami, K. Hashimoto, T. Shibauchi, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, and Y. Matsuda, "Field-induced first-order topological phase transition in a Kitaev spin liquid candidate α-RuCl3"
- K. Fukui, Y. Kato, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Ground state phase diagram of the Kitaev-Heisenberg model with general spin S"
2021 (online)
- Y. Yasui, C. J. Butler, N. D. Khanh, S. Hayami, T. Nomoto, T. Hanaguri, Y. Motome, R. Arita, T. Arima, Y. Tokura, and S. Seki, "Imaging the coupling between itinerant electrons and localised moments in the centrosymmetric skyrmion magnet GdRu2Si2"
- S. Okumura, T. Morimoto, Y. kato, and Y. Motome, "Nonlinear optical responses in chiral magnetic metals"
- K. Shimizu, S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Spin Moire Engineering of Emergent Electromagnetism"
- Y. Kasahara, T. Yokoi, S. Ma, S. Kasahara, T. Shibauchi, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, C. Hickey, S. Trebst, and Y. Matsuda, "Half-integer quantized anomalous thermal Hall effect and topological Chern number in the Kitaev material α-RuCl3"
2020 (Denver, Colorado (cancelled))
- Y. Motome, J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Kato, "Majorana-magnon crossover by a magnetic field in the Kitaev model"
- Y. Yasui, C. Buttler, K. Nguyen, T. Nomoto, S. Hayami, T. Hanaguri, Y. Motome, R. Arita, T. Arima, Y. Tokura, ad S. Seki, "Spectroscopic-imaging STM measurement of magnetic skyrmions in a centrosymmetric crystal"
- S. Okumura, S. Hayami, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic hedgehog lattices in noncentrosymmetric metals"
2019 (Boston, Massachusetts)
- S. Okumura, H. Ishizuka, Y. Kato, J. Ohe, and Y. Motome, "Spin-current diode with a monoaxial chiral magnet"
- N. Mitsuishi, Y. Sugita, S. Bahramy, M. Kamitani, T. Sonobe, M. Sakano, T. Shimojima, K. Horiba, H. Kumigashira, K. Taguchi, K. Miyamoto, T. Okuda, S. Ishiwata, Y. Motome, and K. Ishizaka, "ARPES study on the electronic structure of VTe2 with double zigzag chains"
- Y. Wang, G. B. Osterhoudt, Y. Tian, P. J. Kelley, A. Banerjee, T. A. Goldstein, J. Yan, J. Knolle, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, S. Nagler, D. G. Mandrus, and K. Burch, "High Temperature Fermi Statistics from Majorana Fermions in an Insulating Magnet"
- Y. Shimizu, Y. Nagai, T. Jinno, M. Itoh, J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "NMR observation of field induced fractionalized spin excitations in the Kitaev spin liquid candidate"
- M. Onga, Y. Sugita, T. Ideue, Y. Nakagawa, R. Suzuki, Y. Motome, and Y. Iwasa, "Optical properties of monolayer MoSe2/layered antiferromagnet heterostructures"
- Y. Kato and Y. Motome, "Magnetoelectric properties in antiferromagnets composed of square cupolas A(TiO)Cu4(PO4)4 (A = Ba, Sr, Pb)"
- P. Mishchenko, Y. Kato, K. O'Brien, T. Bojesen, T. Eschmann, M. Hermanns, S. Trebst, and Y. Motome, "Three-dimensional chiral spin liquids in the Kitaev model on a hypernonagon lattice"
- Y. Kamiya, J. Yoshitake, Y. Kato, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Nonlinear magnetic susceptibility in the Kitaev model"
2018 (Los Angeles, California)
- Y. Kasahara, K. Sugii, T. Ohnishi, M. Shimozawa, M. Yamashita, N. Kurita, H. Tanaka, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, T. Shibauchi, and Y. Matsuda, "Observation of half-integer thermal Hall conductance in a Kitaev quantum magnet"
- Y. Sugita, T. Miyake, and Y. Motome, "Multiple Dirac cones and spontaneous quantum anomalous Hall state in monolayer transition metal trichalcogenides"
- S. Okumura, Y. Kato, and Y. Motome, "Numerical study of the electronic state and transport properties in a chiral soliton lattice"
- Y. Motome, "Thermal Fractionalization in Kitaev Quantum Spin Liquids" (invited talk)
2017 (New Orleans, Louisiana)
- J. Nasu, Y. Kato, J. Yoshitake, and Y. Motome, "Liquid-Liquid Transition in Kitaev Magnets Driven by Spin Fractionalization"
- S.-H. Do, S.-Y. Park, J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, Y. Motome, Y. S. Kwon, D. T. Adroja, D. Voneshen, J.-H. Park, K.-Y. Choi, and S. Ji, "The realization of Majorana fermions in Kitaev Quantum Spin Lattice"
2016 (Baltimore, Maryland)
- J. Yoshitake, J. Nasu, and Y. Motome, "Magnetic fluctuations and dynamics in the vicinity of quantum spin liquids: Cluster dynamical mean-field study of the Kitaev model"
- R. Ozawa, S. Hayami, K. Barros, G-W. Chern, Y. Motome, and C. D. Batista, "Vortex Crystals with Chiral Stripes in Itinerant Magnets"
2015 (San Antonio, Texas)
- R. Ozawa, K. Barros, G-W. Chern, S-Z. Lin, M. Udagawa, Y. Motome, and C. D. Batista, "Fermi Surface Induced Scalar Chiral Stripes in the Kondo Lattice Model on a Square Lattice"
2014 (Denver, Colorado)
- S. Hayami, H. Kusunose, and Y. Motome, "Toroidal ordering in metals: band shift, magnetotransport, and magnetoelectric effect"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, "Spin-cluster Formation and Spin-Hall Effect in a Pyrochlore Magnet"
- J. Nasu, T. Kaji, K. Matsuura, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Finite-temperature phase transition to a quantum spin liquid in a 3D Kitaev model"
- R. Ozawa, M .Udagawa, Y. Akagi, and Y. Motome, "Reconstruction of Chiral Edge States in Magnetic Chern Insulators"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, "Loop-liquid State in an Ising-spin Kondo Lattice Model on a Kagome Lattice"
- M Udagawa, "Itinerant spin ice" (invited talk)
2013 (Baltimore, Maryland)
- Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Quantum Fluctuation Effect on a Spin Scalar Chiral Ordering in Frustrated Kondo Lattice System"
- Y. Motome, "Spin-charge interplay on frustrated lattices" (invited talk)
- M. Udagawa, H. Ishizuka, and Y. Motome, "Quantum criticality and fractional charge excitations in itinerant ice-rule systems"
- S. Hayami, T. Misawa, Y. Yamaji, and Y. Motome, "3D Dirac Electrons on a Cubic Lattice with Noncoplanar Multiple-Q Order"
- Y. Motome and H. Ishizuka, "Quantum Topological Hall Effect in Kagome Ice"
- H. Ishizuka and Y. Motome, "Dirac Half-Metal in a Triangular Ferrimagnet"
2012 (Boston, Massachusetts)
- H. Ishizuka, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Monte Carlo study of a spin-ice type Kondo lattice model on a pyrochlore lattice"
- J. Yoshitake, T. Misawa, and Y. Motome, "Cluster dynamical mean-field study of charge ordering in the Kondo lattice model at quarter filling"
- Y. Akagi, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Spin scalar chiral ordering and hidden positive biquadratic interaction in frustrated Kondo lattice systems"
- S. Hayami, M. Udagawa, and Y. Motome, "Partial disorder in the periodic Anderson model on a triangular lattice"
- Y. Motome, M. Udagawa, and H. Ishizuka, "Non-Kondo mechanism of resistivity upturn in a spin-ice Kondo lattice model"
2011 (Portland, Oregon)
- J. Yoshitake and Y. Motome, "Trimer Formation and Metal-Insulator Transition in Triangular-Lattice Systems LiVX2 (X=O,Se,S)"
- Y. Motome, K. Nakamikawa, Y. Yamaji, and M. Udagawa, "Partial Kondo screening in geometrically frustrated Kondo lattice systems"
2010 (Dallas, Texas)
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, "Spin-charge coupled phenomena in Mo pyrochlore oxides under pressure: Monte Carlo study of the double-exchange model on a frustrated pyrochlore lattice"
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Chirality-driven heavy-fermion behavior in kagome Hubbard model"
- T. Ogitsu, F. Gygi, J. Reed, M. Udagawa, Y. Motome, E. Schwegler, and G. Galli, "Geometrical frustration and macroscopic residual entropy in an elemental boron explained by a frustrated Ising model"
2009 (Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania)
- Y. Motome and N. Furukawa, "Phase competition and large residual entropy in the pyrochlore double-exchange system"
2008 (New Orleans, Louisiana)
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Magnetic Fluctuations in the Hubbard Model on Kagome-based Frustrated Lattices"
- H. Seo and Y. Motome, "Charge frustration and novel electron-lattice coupled phase transition in organic conductor DI-DCNQI2Ag"
- Y. Otsuka, H. Seo, Y. Motome and T. Kato, "Numerical Study of Finite-Temperature Phase Transitions in Quasi-One-Dimensional Molecular Conductors"
2007 (Denver, Colorado)
- M. Udagawa and Y. Motome, "Coexisting fluctuations of charge ordering in quasi-2D organic conductors, theta-(ET)2X"
- H. Seo, Y. Motome and T. Kato, "Finite-Temperature Phase Transitions in Quasi-One-Dimensional Molecular Conductors"
FY2025
- 葛西章也, "トポロジカル磁気渦糸のねじれ欠陥ダイナミクス", 第31回渦糸物理ワークショップ (VPWJ2025) (2025年12月, 東京大学柏図書館メディアホール)
- 求 幸年, "Magnetic hopfions: Crystallization and dynamics", 学術変革領域研究(A)「相関設計で挑む量子創発」2025年領域会議 (2025年12月, 理研・和光)
- 求 幸年, "第三の磁性体?「交替磁性体」", 第6回パイロクロア研究会(2025年10月, 九工大)
- 求 幸年, "第三の磁性体「交替磁性体」", 令和7年度 東北大学電気通信研究所 共同プロジェクト研究会「量子技術と物質科学の融合による次世代デバイスの創製」(2025年10月, 松島)
- 小林海翔, "Quantum reservoir probing: exploration of quantum many-body physics via computational performance", 東京大学物性研究所理論セミナー (2025年7月, 東京大学物性研究所)
FY2024
- 求 幸年, "キタエフスピン液体の物質設計", 第1回熊本大学物性物理セミナー (2024年12月, 熊本大学)
- 福井 毅勇, "汎関数繰り込み群によるキタエフスピン液体実現可能性の研究", 第20回量子スピン系研究会 (2024年12月, あきた芸術村 温泉ゆぽぽ)
- 求 幸年, "量子スピン液体に現れるマヨラナ粒子", 第29回 CROSSroads Workshop「固体化学と固体物理の先端的量子ビーム利用研究」 (2024年10月, AYA’S LABORATORY量子ビーム研究センター)
- 求 幸年, "スピン液体の物理", 第69回物性若手夏の学校 (2024年8月, ホテルたつき)
FY2023
- 求 幸年, "Search for spin liquid crystals: insight from Skyrme and Kitaev", 令和5年度 新学術領域研究「量子液晶の物性科学」領域研究会 (2023年12月, 東京大学物性研究所)
- 奥村 駿, "3次元トポロジカル磁性金属における電磁気応答とスピンモアレエンジニアリング", 東北大学理学研究科 物性コロキウム (2023年12月, 東北大学)
- 求 幸年, "スピンモアレエンジニアリンク", 令和5年度 東北大学 電気通信研究所 共同プロジェクト研究会 「量子物質の制御と機能開拓およびそのデバイス応用」(2023年10月, 仙台)
FY2022
- 求 幸年, "Kitaevスピン液体とエニオン"(チュートリアル講演), 物性研短期研究会「固体におけるエニオンと分数統計粒子研究の最前線」 (2023年2月, 東京大学物性研ハイブリッド開催)
- 求 幸年, "Kitaev magnets as a Majorana platform", 107th RIKEN CEMS Colloquium (2022年12月, 理化学研究所ハイブリッド開催)
- 求 幸年, "量子スピン液体:磁性とトポロジーが出会う不思議な量子状態", 日本物理学会第12回オンライン物理講話 (2022年12月, オンライン)
- 加藤康之, "創発磁気モノポール格子における隠れたトポロジカル転移の理論解析", ISSPワークショップ「カイラル物質科学の新展開」 (2022年12月, 東大物性研ハイブリッド開催)
- 求 幸年, "Spin nematics meet spin liquids: numerical study of the S=1 Kitaev model with biquadratic interactions", 令和4年度 新学術領域研究「量子液晶の物性科学」領域研究会 (2022年12月, 名古屋大学ハイブリッド開催)
- Rico POHLE, "Spin liquid and nematic states in the spin-1 honeycomb Kitaev model with bilinear-biquadratic interactions", 新学術領域研究「量子液晶の物性科学」第7回QLC若手コロキウム (2022年5月, オンライン開催)
- 求 幸年, "電子相関とフラストレーションがもたらす新しい量子物性", 「新物質開発の展開と展望」ワークショップ (2022年5月, オンライン開催)
FY2021
- 求 幸年, "Phase shift in topological spin crystals", 令和3年度 新学術領域研究「量子液晶の物性科学」領域研究会 (2022年2月, オンライン開催)
- Rico POHLE, "Dynamics of quantum liquid crystals from numerical simulations", 新学術領域研究「量子液晶の物性科学」第4回QLC若手コロキウム (2021年9月, オンライン開催)
- 奥村 駿, "金属磁性体に現れる磁気ヘッジホッグ格子の理論研究", 新学術領域研究「量子液晶の物性科学」第3回QLC若手コロキウム (2021年6月, オンライン開催)
- 清水宏太郎, "多重Qトポロジカル磁気テクスチャにおけるフェーゾン", 新学術領域研究「量子液晶の物性科学」第2回QLC若手コロキウム (2021年4月, オンライン開催)
FY2020
- Y. Motome, "Spin moire and emergent topology", CREST Workshop on "Physics of helical and skyrmion phases" (2021年3月, オンライン開催)
- 求 幸年, "Spin moire superstructure", 新学術領域研究「量子液晶の物性科学」令和2年度 領域研究会 (2020年12月, オンライン開催)
- 清水宏太郎, "スピンモアレによる創発電磁場とトポロジカル転移", 第14回 物性科学領域横断研究会 (2020年11月, オンライン開催)
- 清水宏太郎, "スピンモアレによる創発電磁場とトポロジカル転移", 新学術領域研究「量子液晶の物性科学」量子物質開発フォーラム (2020年10月, オンライン開催)
FY2019
- 加藤康之, "ハイパーノナゴン格子キタエフ模型の3次元カイラルスピン液体", 第14回量子スピン系研究会 (2020年1月, あきた芸術村 ゆぽぽ)
- 求 幸年, "Kitaevスピン液体におけるマヨラナ励起の検証:現状と今後", 新学術領域研究「トポロジーが紡ぐ物質科学のフロンティア」第12回トポロジー連携研究会「マヨラナ励起の実証に向けて」(2019年11月, 東工大大岡山キャンパス)
- 求 幸年, "磁性体に現れるマヨラナ粒子", 令和元年度 東北大学 電気通信研究所 共同プロジェクト研究会 「固体素子における非平衡ダイナミクスの精緻な理解と機能開拓」(2019年11月, 仙台)
- 求 幸年, "Spin liquid crystals: some hints from Skyrme and Kitaev", 新学術領域研究「量子液晶の物性科学」キックオフミーティング (2019年8月, 東京大学浅野キャンパス)
FY2018
- 求 幸年, "分裂するスピン", 第43回Kyutech物性セミナー ・応用物理学会特別講演会 (2019年3月, 九州工業大学戸畑キャンパス)
- Y. Motome, "Majorana fermions in topological magnets", AIMR Tea Time Talk (2018年12月, 東北大学材料科学高等研究所)
- 求 幸年, "スピン軌道結合によるトポロジカル物性設計", ISSPワークショップ「スピン軌道強結合伝導系におけるサイエンスの新展開」(2018年11月, 東京大学物性研究所)
- 加藤 康之, "反強磁性正四角台塔系の磁化過程と電気磁気応答", 基研研究会「スピン系物理の最前線」(2018年10月-11月, 京都大学基礎物理学研究所)
- 張 成燻, "f電子系におけるキタエフスピン液体の物質設計", 基研研究会「スピン系物理の最前線」(2018年10月-11月, 京都大学基礎物理学研究所)
- 求 幸年, "磁性体中に現れるマヨラナ粒子", ワークショップ「物性理論のフロンティアと社会への展開」(2018年5月, 東京大学本郷キャンパス)
FY2017
- 求 幸年, "分裂する電子スピンが引き起こす新しい量子磁性現象", 平成29年度 東北大学 電気通信研究所 共同プロジェクト研究会 「電荷とスピンの制御に基づく精密物性科学の構築とデバイス応用」(2017年11月, 仙台)
- 求 幸年, "電子相関が引き起こすスピン軌道物性", ISSPワークショップ「5dパイロクロア酸化物研究における最近の展開」(2017年8月, 東大物性研)
FY2016
- 求 幸年, "分数スピンが引き起こす新しい相転移", 第5回パイロクロア研究会(2016年12月, 岡山大学)
- 求 幸年, "スピンの自由度が分数化すると何が起きるのか", 平成28年度 東北大学 電気通信研究所 共同プロジェクト研究会 「電荷とスピンの制御に基づく精密物性科学の構築とデバイス応用」(2016年11月, 仙台)
- 求 幸年, "量子スピン液体の現状と将来 ー Kitaevモデルを軸とした新展開", ワークショップ:物性物理・現状と将来 (2016年6月, 秋田大学)
- 小澤 遼, "遍歴磁性体における多項式展開法を用いた高効率シミュレーションによる新奇な非共面的磁気秩序状態の探索", 物性研究所スパコン共同利用・CCMS合同研究会「計算物質科学の今と未来」 (2016年4月, 東京大学物性研究所)
FY2015
- 求 幸年, "量子スピン液体におけるスピン分数励起", 新学術領域研究「トポロジーが紡ぐ物質科学のフロンティア」第1回領域研究会 (2015年12月, 京都大学芝蘭会館 稲盛ホール・山内ホール)
- 求 幸年, "数値実験で観る磁性体の新しい量子物性", 東京大学物性研究所短期研究会「量子物質研究の最前線」 (2015年12月, 東京大学物性研究所)
- 加藤 康之, "J1-J2横磁場イジング模型における量子三重臨界点の量子モンテカルロシミュレーション", 東京大学物性研究所短期研究会「スピン系物理の深化と最前線」 (2015年11月、東京大学物性研究所)
- 吉竹 純基, "量子スピン液体近傍の磁気揺らぎとダイナミクス:Kitaev模型に対するクラスター動的平均場近似による研究", 東京大学物性研究所短期研究会「スピン系物理の深化と最前線」 (2015年11月、東京大学物性研究所)
FY2014
- 求 幸年, "Fractionalization of quantum spins into Majorana fermions, and beyond", 物性理論・統計力学セミナー2015 (2015年3月、ラフォーレ倶楽部 箱根強羅)
- 求 幸年, "スピン液体とトポロジー:局所拘束条件と局所保存量の観点から", 基礎物理学研究所研究会「量子多体系研究の新しい潮流 - テンソルネットワーク・繰り込み群・エンタングルメント -」 (2014年12月、京都大学基礎物理学研究所)
- 求 幸年, "スピン軌道相互作用に起因した特異な磁性と伝導現象 - トロイダル金属が示す新しい量子伝導 -", 物性ワークショップ「強くスピン軌道相互作用した強相関電子系における新奇量子相と量子現象」 (2014年11月、九州工業大学)
- 宇田川 将文, "パイロクロア伝導系のトポロジカル欠陥", 物性ワークショップ「強くスピン軌道相互作用した強相関電子系における新奇量子相と量子現象」 (2014年11月、九州工業大学)
- 速水 賢, "遍歴電子系における特異な磁性と電子状態 - 多重Q秩序、ディラック電子、磁気的なトポロジカル絶縁体 -", 日本物理学会北海道支部講演会 (2014年10月、北海道大学)
- 宇田川 将文, "パイロクロア伝導系のトポロジカル欠陥", 研究環「特異な結晶構造に創出する新奇量子相の解明」第2回研究会 (2014年9月、首都大学東京)
- 求 幸年, "All-in/all-out 絶縁体の磁壁における磁性と電子状態", CMRCミニ研究会「5d遷移金属化合物における金属-絶縁体転移」 (2014年6月、高エネルギー加速器研究機構)
FY2013
- 求 幸年, "量子スピン液体の気液相転移?", 物性理論・統計力学セミナー2014 (2014年3月、ラフォーレ修善寺)
- 求 幸年, "拡張多極子クラスターによる新しい量子伝導現象", 物性研究所 短期研究会「強相関電子系における局所対称性の破れと量子物性」 (2013年11月、東京大学物性研究所)
- 求 幸年, "スピンアイス伝導系が示す特異な量子伝導", 物性研究所 計算物質科学研究センター(CCMS) 第3回シンポジウム「スピン・軌道相互作用の物理における実験・理論・計算」 (2013年11月、東京大学物性研究所)
- 求 幸年, "スピンアイス伝導系の異常量子伝導", 第1回パイロクロアワークショップ「高対称格子上の変幻自在電子」 (2013年7月、北海道大学)
FY2012
- 求 幸年, "近藤格子系における電荷秩序不安定性", 新学術領域研究「重い電子系の形成と秩序化」第4回研究会 (2013年1月、東京工業大学)
FY2011
- 求 幸年, "多項式展開モンテカルロ法によるスピン電荷結合系の数値的研究", 「強相関系に対する計算科学手法とその応用」に関する研究会 (2012年1月、東京大学工学部8号館、6号館)
- 求 幸年, "Mo パイロクロア系の理論 — 異常金属状態,金属絶縁体転移, スピングラス転移", KEK/物構研 CMRC 研究会「遍歴系における幾何学的電子相関」 (2012年1月、つくば国際会議場)
- 求 幸年, "フラストレート伝導系に現れる非自明な秩序 ーカイラリティ、部分無秩序、スピンアイスー", 東京大学物性研究所 理論セミナー (2011年12月、東京大学物性研究所)
- 吉竹純基, "軌道縮退した三角格子系LiVX2 (X=O,S,Se)における三量体形成と金属絶縁体転移", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:フラストレーションが創る新しい物性 第7回トピカルミーティング「フラストレーションとスピン・電荷・軌道・格子自由度」 (2011年7月、彦根ビューホテル)
- 求 幸年, "近藤格子系における電荷密度波形成の高精度変分モンテカルロ法による研究", 新学術領域研究「重い電子系の形成と秩序化」第3回研究会 (2011年6月、東京大学物性研究所)
- 求 幸年, "スピン電荷結合系におけるフラストレーションと新奇な磁性・伝導現象", FIRSTプログラム「強相関量子科学」理論フォーラムワークショップ「スピン物性物理学の将来展望」 (2011年4月、東京大学工学部6号館)
FY2010
- 求 幸年, "多項式展開モンテカルロ法の現状と今後の展望", CMSI研究会:第1部会「新量子相・新物質の基礎科学」 (2010年11月、自然科学研究機構 岡崎コンファレンスセンター)
- 求 幸年, "フラストレート近藤格子系における部分近藤スクリーニング", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:フラストレーションが創る新しい物性 第6回トピカルミーティング「フラストレーションと量子輸送」 (2010年10月、宮島グランドホテル)
- 求 幸年, "フラストレーションのある強相関電子系における相競合", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:フラストレーションが創る新しい物性 平成22年度立ち上げ全体会議 (2010年5月、理化学研究所)
- 求 幸年, "パイロクロア格子系のフラストレーションによる縮退とその解放", CMRC研究会「相関電子と構造物性」 (2010年2月、高エネルギー加速器研究機構)
FY2009
- 宇田川将文、 "フラストレート伝導電子系における''ice rule''局所拘束条件の効果", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:フラストレーションが創る新しい物性 平成21年度領域成果報告会 (2010年1月、京都大学基礎物理学研究所)
- 求 幸年, "フラストレート分子性導体(DI-DCNQI)2Agにおける電荷とボンドの秩序", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:フラストレーションが創る新しい物性 第5回トピカルミーティング「誘電体にひそむランダムネスとフラストレーション」 (2009年12月、大阪大学豊中キャンパス)
FY2008
- 求 幸年, "三角格子上の強相関電子系におけるスピンフラストレーション、電荷・スピン・軌道秩序と金属絶縁体転移", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:フラストレーションが創る新しい物性 平成20年度領域成果報告会 (2009年1月、東京大学物性研究所)
- 求 幸年, "Spiral charge frustration in quasi-1D molecular conductor (DI-DCNQI)2Ag", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:異常量子物質の創製 -新しい物理を生む新物質- 2008年度成果報告会 (2009年1月、東京大学生産技術研究所)
- 求 幸年, "フラストレート遍歴電子系における相競合と新奇な伝導現象", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:フラストレーションが創る新しい物性 第3回トピカルミーティング「フラストレーションとスピン液体」 (2008年12月、神戸大学百年記念館六甲ホール)
- 求 幸年, "Monte Carlo study of double-exchange model on the 3D frustrated pyrochlore lattice: finite-size effect and averaging over twisted boundary conditions", 次世代ナノ情報機能・材料グループ成果報告会 (2008年12月、東北大学金属材料研究所)
- 宇田川将文, "クラスター動的平均場理論によるハイパーカゴメ格子上ハバードモデルの解析", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:異常量子物質の創成 「新しい物理を生む 新物質若手の会 第四回会議」 (2008年11月、箱根パークス吉野)
- 求 幸年, "三角格子系LiVO2における三量体化の起源", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:フラストレーションが創る新しい物性 「平成20年度立ち上げ全体会議」 (2008年6月、理化学研究所 和光研究所)
- 求 幸年, "フラストレート電子系におけるスピンと電荷の揺らぎ", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:スーパークリーン物質で実現する新しい量子相の物理 「A01&A05班合同研究会」 (2008年5月、東京大学小柴ホール)
FY2007
- 求 幸年, "分子性導体の示す相競合の数値的研究", 「次世代ナノ情報機能・材料」成果報告会プログラム (2008年2月、御茶の水ビジネスセンター)
- 宇田川将文, "カゴメおよびハイパーカゴメ格子上のハバードモデルにおける磁気ゆらぎと強相関効果", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:フラストレーションが創る新しい物性 「第1回トピカルミーティング」 (2008年1月、京大会館)
- 求 幸年, "スピネルおよび関連物質における複合自由度の競合", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:フラストレーションが創る新しい物性 「キックオフミーティング」 (2007年11月、大阪大学中之島研修センター)
FY2006
- 求 幸年, "強相関電子系のモデル計算におけるモンテカルロシミュレーション", 物性研究所短期研究会「計算物性科学におけるスーパーコンピュータ利用の現状と展望」 (2006年12月, 東京大学物性研究所)
- 宇田川将文, 求 幸年, "θ型ET塩における水平電荷秩序の抑制と異なる波数をもった揺らぎの共存", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:新しい環境下における分子性導体の特異な機能の探求 「新物性の理論研究会」 (2006年11月, 東京大学)
- 求 幸年, "有機サイリスタθ-ET塩における電荷揺らぎの共存のメカニズム", 理研シンポジウム 第2回電子複雑系科学研究会「電子複雑系の機能と物性開拓」 (2006年10月、理化学研究所)
- 求 幸年, "Macroscopic degeneracy and exotic states in pyrochlore Heisenberg antiferromagnets", 文部科学省科学研究費補助金特定領域研究:スーパークリーン物質で実現する新しい量子相の物理 「A01&A05研究項目合同ワークショップ」 (2006年7月、那須ビューホテル)
- Y. Motome, "Frustration and multiple degrees of freedom in spinel oxides", 'MPI-ERATO-BUTSUKO Workshop on Spin-Charge-Orbital Correlated Phenomena' (Jun. 2006, Univ. of Tokyo)
Thesis
| Doctor Theses (click to show/hide) |
|
|---|
| Master Theses (click to show/hide) |
|
|---|
Lecture Click the thumbnail to show/hide the description below.
| Computational Physics | Graduate | 2025- | Introduction to the computational condensed matter physics including various computational methods |
|
|||
| Statistical Mechanics II | undergraduate | 2023- | Fundamental understanding of phase transitions, critical phenomena, linear response, and stochastic processes |
|
|||
| Solid State Physics II | undergraduate | 2015-2022, 2024 | Fundamentals of physical properties in solids: electron motion and transport phenomena, semiconductors, optical properties, magnetism |
|
|||
| Solid State Physics III | undergraduate | 2011-2014 | Fundamentals of many-body quantum theory: many electrons, many bosons, electron-phonon coupling, superconductivity |
|
|||
| Solid State Physics IV/Condensed Matter Physics | undergraduate/graduate | 2006-2009- | Many-body problem in solid state physics: Magnetism in localized electron systems and itinerant electron systems |
|
|||
| Applied physics learning from Nobel prizes | undergraduate | 2014-2019, 2022- | Physical background and development in the Nobel Prizes in Physics over the past 40 years |
|
|||
| Applied Physics Seminar | undergraduate | 2006, 2012 | Group work on reading, giving a presentation, and discussing text books and original papers |
|
|||
| Mathematics 1 | undergraduate | 2006, 2007, 2010 | Ordinary differential equations, vector analysis, and variational methods |
|
|||
| Mathematics 2 | undergraduate | 2009, 2011, 2013, 2015, 2017, 2019-2022 | Fourier-Laplace analysis, and partial differential equations |
|
|||
| Intensive courses (click to show/hide) |
|
|---|
Access
Faculty of Engineering Bldg. 6, Department of Applied Physics, University of Tokyo, Hongo 7-3-1, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656, JAPAN